Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and it can lead to numerous health complications if not managed properly. This condition hinders the body’s ability to produce insulin, a hormone that regulates glucose (sugar) levels in the blood.
Without adequate insulin, blood sugar levels remain high, leading to a host of problems. High blood sugar can damage the body’s blood vessels, nerves, and organs, and increase the risk of developing serious complications such as heart disease, nerve damage, kidney disease, and diabetic wounds. In this blog post, we will explore the link between diabetes and slow wound healing and provide valuable insights into managing this condition to prevent complications.
Diabetic wounds can be a great problem, especially for seniors, as the skin become thinner and loses its elasticity, making it more susceptible to injuries. These wounds are injuries or cuts that are slow to heal in people with diabetes. Although cuts, scrapes, scratches, and blisters can occur anywhere in the body, they are commonly found on the feet and lower legs. A small wound on the foot can quickly develop into a foot ulcer- turning it into a potentially life-threatening problem.
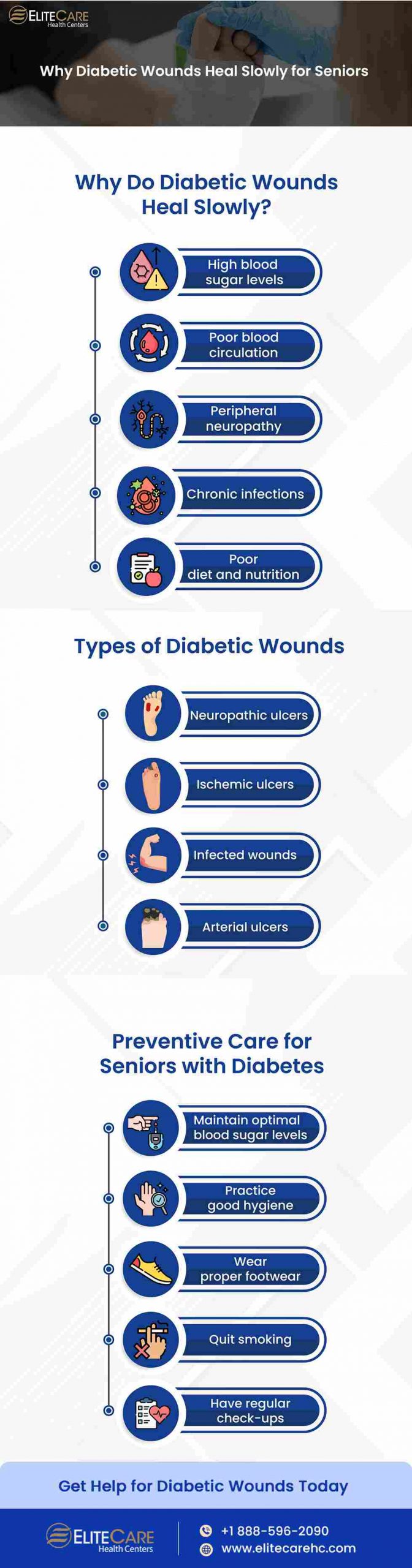
Why is Wound Healing Slow?
A. Hyperglycemia
Also known as high blood sugar level, is a major cause of slow diabetic wound healing. When blood sugar levels are elevated, it can damage the blood vessels that supply blood to the wound, reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the wound and increasing the inflammation of the body’s cells.
B. Poor blood circulation
It is one of the common causes of slow diabetic wound healing. Diabetes damages the blood vessels, reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the wound. This can cause the healing process to slow down, as the wound does not receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen to heal.
C. Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, or nerve damage, occurs due to high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period. It damages vessels and nerves. This causes the affected area to lose its sensation. Neuropathy mostly occurs in the hands and feet. Even small cuts or wounds go unnoticed leading to slow healing and increased risk of infections.
D. Chronic infections
The increased sugar level in the bloodstream creates a favorable environment for bacteria to grow, which can lead to chronic infections. With age, the immune system weakens, making it more difficult for seniors to fight off infections. Seniors should seek medical attention promptly- if they notice any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage from the wound.
F. Other factors
Poor diet and nutrition, smoking, and aging can contribute to slow diabetic wound healing in seniors. A diet lacking essential nutrients and vitamins weakens the immune system and reduces the body’s ability to heal. Smoking reduces the blood flow to the wound, slowing down the healing process.
Read More: Foods That Help Lower Blood Pressure
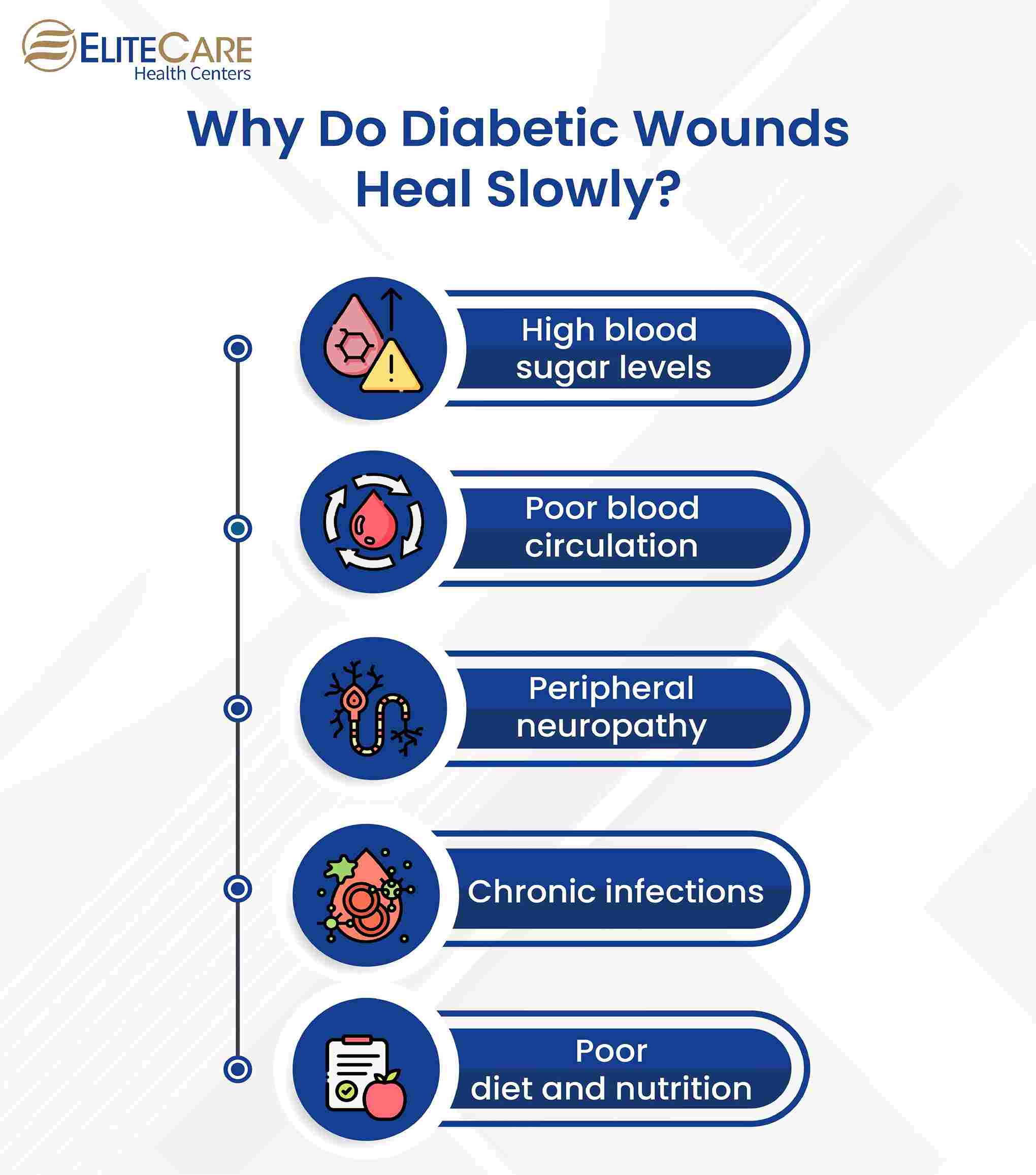
Types of Diabetic Wounds
- Neuropathic ulcers are caused by nerve damage and are typically found on the feet.
- Ischemic ulcers are caused by poor blood flow and are typically found on the lower legs.
- Infected wounds are caused by bacterial infections and can occur anywhere on the body.
- Arterial ulcers caused by poor blood flow due to narrowed or blocked arteries are typically found on the toes or shin.
What Happens If the Wounds Are Untreated
Diabetic wounds left untreated can cause serious complications such as infections and gangrene- a death of body tissue due to lack of body supply. Untreated wounds spread, causing the affected limb to become infected, swollen, and painful. This can eventually lead to sepsis, a severe and potentially life-threatening condition. In some cases, the infection may even spread to the bones, causing osteomyelitis, which can lead to amputation and greatly impact the senior’s mobility and quality of life. The longer a diabetic wound goes untreated, the more severe the consequences can become, making it critical for seniors with diabetes to seek medical attention for the wounds that are not healing as soon as possible.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Wounds in Seniors
The best way to ensure seniors are protected from serious injury is to prevent wounds. If there is a cut or scrape, treat the wound immediately. If there is a worse or deeper wound, the treatment depends on the person’s condition and may require the following treatment options. The best treatment plan for the wound depends on the senior’s health condition and may involve a combination of the following treatment options. Additionally, a healthcare professional should be consulted to determine the best course of action.
1. Medical treatments
This involves using medications, such as antibiotics, to reduce inflammation, treat infections, and manage pain. In some cases, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) may also be used, exposing the patient to high oxygen levels in a pressure room or small chamber. Evidence suggests that HBOT improves blood flow to the affected area and enhances wound healing.
2. Topical creams and ointments
These are applied directly to the wound and can help to prevent infections, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. Some common examples include topical antibiotics, wound dressings, and moisture-retentive ointments. In some cases, special wound care products, such as hydrogels or growth factor products, may be recommended by medical clinic to improve healing and reduce scarring.
3. Offloading devices
The goal of offloading is to reduce the pressure on the affected area, which can help to prevent further injury and promote healing. Offloading devices can include special shoes or inserts, wound dressings, or cast walkers. For example, special shoes with a rocker bottom design can help to redistribute pressure away from the affected area, while cast walkers can provide complete offloading of the affected area. The type of offloading device used will depend on the physician’s prescription, specific needs, and the wound’s location.
4. Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove dead or infected tissue to prevent further complications. Several surgical procedures may be used to treat diabetic wounds, including debridement, skin grafting, and flap surgery. Surgery is an invasive treatment with risks, such as bleeding, infection, and scarring. It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of surgery with a healthcare provider and carefully consider all available treatment options before making a decision. In some cases, surgery may be the best option to manage diabetic wounds in seniors, but in other cases, other treatment options may be more appropriate.
5. Lifestyle changes
Making changes to one’s lifestyle, such as maintaining a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress, can help to improve overall health and promote the healing of diabetic wounds. Additionally, regular foot care is essential for people with diabetes to prevent and manage possible complications of wounds and injuries.
Read More: Can seniors do strength training exercises?
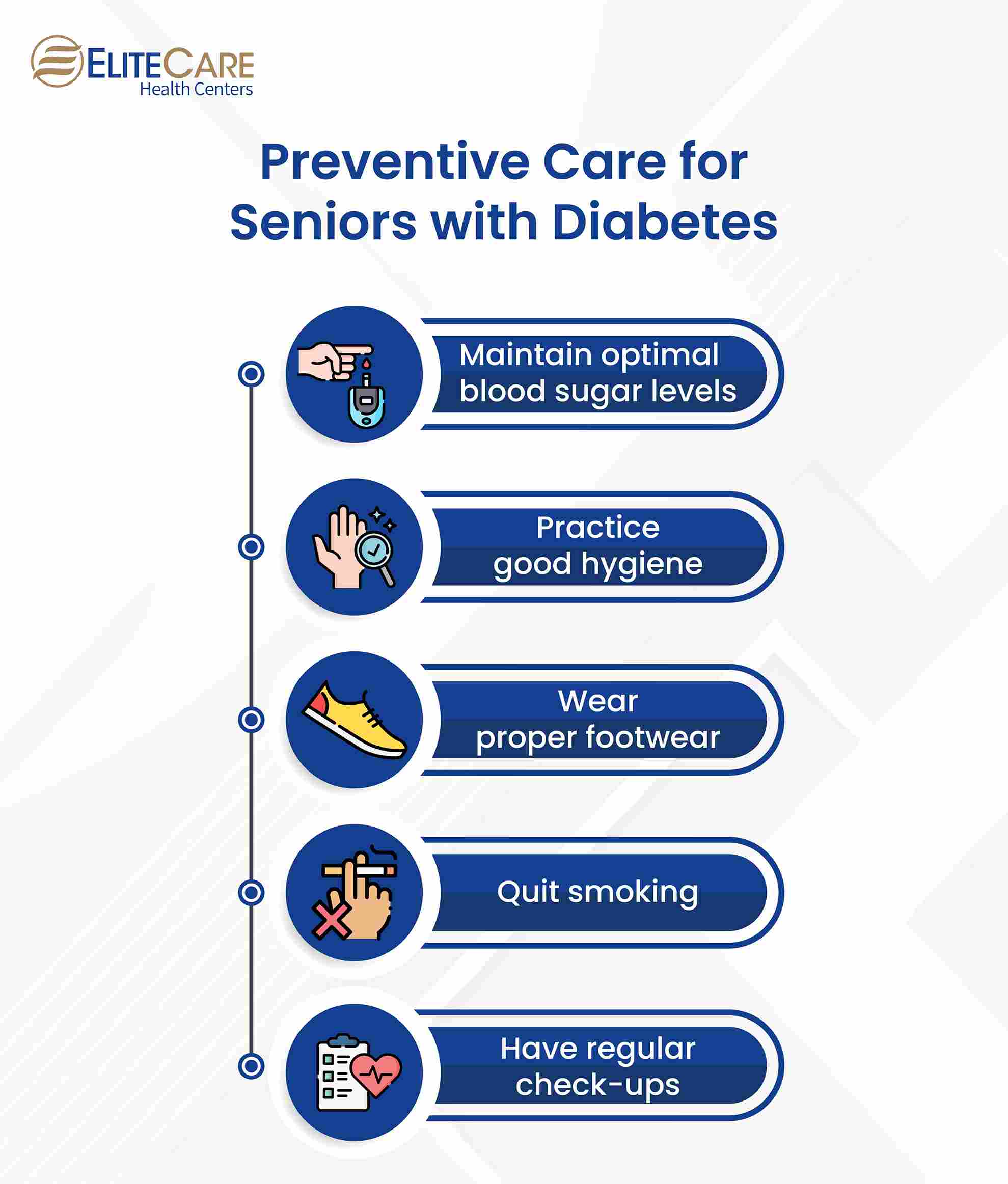
Preventive Care for Seniors with Diabetes
Prevention is key, and there are several steps seniors with diabetes can take to reduce their risk of developing wounds. Some preventive suggestions include:
- Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels within the target range to help prevent diabetic complications, including wounds. This involves monitoring blood sugar regularly, taking medications as prescribed, and following a healthy diet.
- Maintaining good hygiene practices, including regular foot and skin care, such as washing feet daily and keeping them dry, is essential to prevent infections. It’s also important to promptly treat any cuts or scrapes to avoid further complications.
- Wearing comfortable, well-fitting shoes can provide adequate support to help properly reduce the risk of foot injuries, including blisters and sores. It is also important to check the inside of shoes regularly for any foreign objects that could cause injury.
- Quitting smoking can help improve overall health and reduce the risk and complications of diabetes.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help to detect potential complications early, allowing for prompt treatment and reducing the risk of more serious problems. During these check-ups, healthcare providers can monitor blood sugar levels, check for signs of neuropathy and other complications, and advise lifestyle changes to manage diabetes.
Conclusion
Even a small scrape can turn into a serious challenge if not taken care of. Seniors with diabetes should work closely with the EliteCare primary service providers to keep a check on blood sugar levels and to take a proactive approach to manage their condition, which includes enabling healing, reducing the risk of complications, and improving their quality of life in dealing with diabetic wounds.