Type 2 diabetes is a condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate sugar levels in the bloodstream. The hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas, enables blood sugar to enter cells in the body and be utilized as energy. Individuals with type 2 diabetes are insulin resistant, which means that their cells don’t respond properly to insulin. In an attempt to stimulate a response, the pancreas produces more insulin. When the pancreas is no longer able to keep up, blood sugar levels rise beyond normal limits. This can lead to prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Approximately 33% of Americans are expected to be diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes over the course of their lifetime, and an additional 54 million are already considered pre-diabetic. Moreover, the prevalence of this condition increases significantly as people age, which additionally puts seniors at risk for developing heart disease, kidney disease, vision loss and a host of other health problems.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
There are several risk factors which can increase seniors’ likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. Some of them are:
- Being overweight or obese
- Lack of exercise
- Poor diet
- High blood pressure
- Family history of diabetes
- Having prediabetes
Read More: Foods That Help Lower Blood Pressure
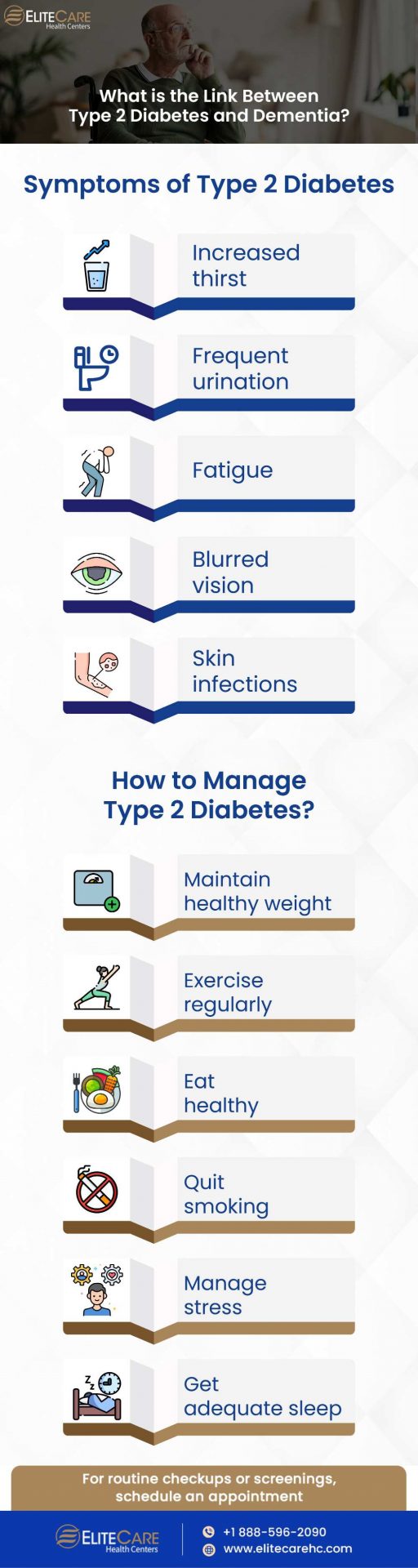
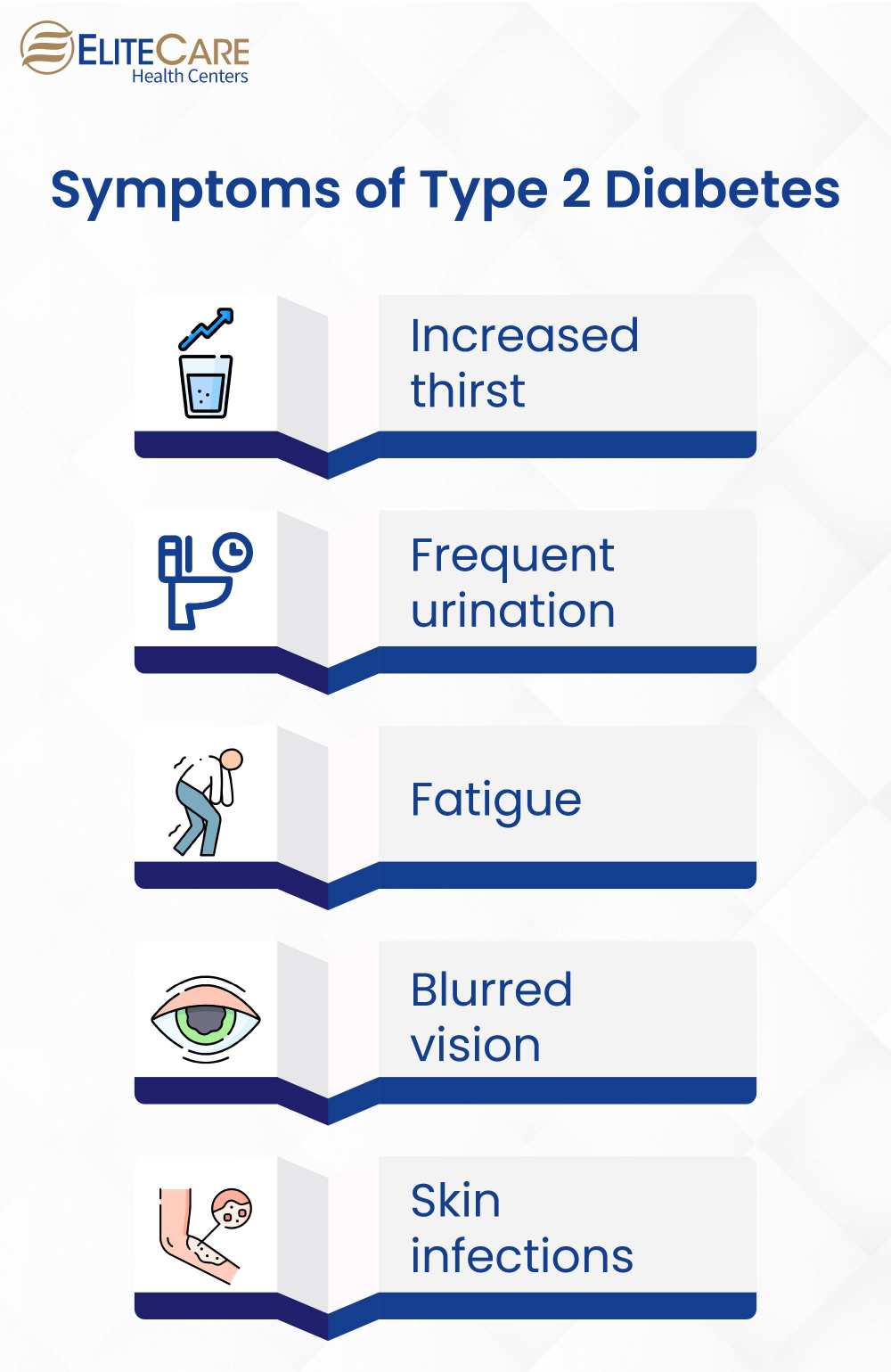
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Seniors who are at risk for type 2 diabetes typically experience symptoms that are similar to those seen in younger individuals, but they may be less noticeable, especially if they have other health issues. Symptoms of this condition include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Skin infections
It is known that type 2 diabetes can increase seniors’ risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, dental problems, skin infections and more. However, recent studies have also discovered a link between type 2 diabetes and dementia. But how are these two diseases connected? Let’s find out.
In 2011, Japanese scientists looked into a longitudinal study on heart disease and stroke, which had been ongoing since 1961. In 1988, over 1000 participants from the study had consented to undergo a glucose tolerance test to determine their ability to process sugar. Over the next 15 years, the researchers monitored these individuals and found that 23.2% of them who suffered from type 2 diabetes had also developed dementia.
Similarly, in another study, researchers examined the link between type 2 diabetes and dementia through a large cohort study which had first started in 1985. Over 30 years later, when the researchers went back to collect data on diabetes exposure, they learned that 37% of those who suffered from type 2 diabetes also suffered from dementia.
In recent years, the correlation between type 2 diabetes and dementia has become stronger. Research has shown that older adults with type 2 diabetes are more likely to develop dementia. Furthermore, these studies have revealed that individuals who develop diabetes at a younger age may face a higher risk of developing dementia. But how does it work?
How Does Type 2 Diabetes Cause Dementia in the Elderly?
There are several reasons why people suffering from type 2 diabetes may be at risk of developing dementia in their later years. One reason being, individuals with type 2 diabetes tend to suffer from hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Frequent episodes of hypoglycemia are known to damage the hippocampus, the part of the brain that is responsible for learning and memory. This can cause memory loss and dementia in seniors who suffer from type 2 diabetes.
Secondly, insulin plays a huge role in the formation of amyloid plaques in the brain. It also contributes to the process which creates neurofibrillary tangles. These plaques and tangles are responsible for the development of Alzheimer’s disease in senior citizens.
Lastly, chronic diabetes can give rise to heart diseases and hypertension, both of which increase the risk of stroke in the elderly. Seniors who have experienced strokes are at a greater risk of developing dementia.
Given the compelling evidence that shows a link between type 2 diabetes and dementia, it is important for seniors to take certain measures to manage diabetes.
How to Manage Type 2 Diabetes in Senior Citizen?
There are several steps that seniors can take to manage type 2 diabetes:
Maintain a healthy weight
Losing weight and maintaining a healthy BMI can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Exercise regularly
Regular physical activity can help reduce insulin resistance and lower the risk of heart disease in the elderly. Even 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity, such as brisk walking, every other day can make a big difference.
Eat a healthy diet
Eating a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help release sugar more slowly into the bloodstream. It is also important to limit the amount of added sugars, saturated fats, and trans fats in the diet.
Quit smoking
Smoking can damage the blood vessels and make it harder to control blood sugar levels. However, quitting cigarettes at any point in their lives can help people add up to 10 years to their lives.
Manage stress
Chronic stress can increase blood sugar levels and put a massive strain on the pancreas and other vital organs. Practice deep breathing, yoga or meditation to keep stress under control.
Get enough sleep
Sleeping for 7-8 hours each night can greatly reduce insulin resistance in people suffering from type 2 diabetes.

By making these lifestyle changes and undergoing regular check-ups with their healthcare provider, seniors can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve their overall health and well-being.
Most elderly individuals with diabetes have type 2 diabetes because of a combination of elevated insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. While it’s not possible to cure it entirely, seniors who take steps to manage their condition can lead healthy lives.
Conclusion
About 61% of healthcare costs associated with diabetes are utilized in the care and treatment of seniors who are 65 or older. Moreover, the cost of diabetes care in older adults is expected to triple between the years 2009 to 2034. Not only is type 2 diabetes costly for the healthcare system but the potential health complications stemming from this condition can significantly increase mortality rates in the elderly. This is why it is so important for seniors to proactively work towards beating this illness and improving the quality of their lives.
If you or your elderly loved one is at risk for type 2 diabetes, visit the nearest EliteCare clinic for a blood sugar test. EliteCare is one of Florida’s best medical clinics, with a team of highly trained primary care physicians who offer services like venipuncture, immunizations, EKG and more. Visit their website to schedule an appointment today.