Frequent urination is a symptom characterized by the need to urinate more often than usual. It increases the urge to pass urine throughout the day and sometimes even at night, disrupting regular sleep patterns. It is a common problem, especially among seniors, and can cause significant inconvenience and disruption to their daily lives.
Frequent urination can indicate several underlying health conditions, and treatment options differ depending on the cause. Here, we will share the causes of frequent urination and how it can be treated or managed. Read on to learn more.
Is Frequent Urination a Normal Part of Aging?
Although frequent urination can be more common among seniors, it is not inherently a normal part of aging. Age-related changes in the urinary system, such as reduced capacity of the bladder to hold urine, weakened pelvic floor muscles, or urinary incontinence, may increase the possibility of frequent urination in people over 60.
However, while these factors may contribute to increased urinary frequency in older individuals, frequent urination can also indicate underlying medical conditions, including infections, diabetes, or prostate problems, which are not related to aging. Therefore, if an older person experiences frequent urination, they should consult a primary care physician to rule out any underlying health concerns.
Causes of Frequent Urination
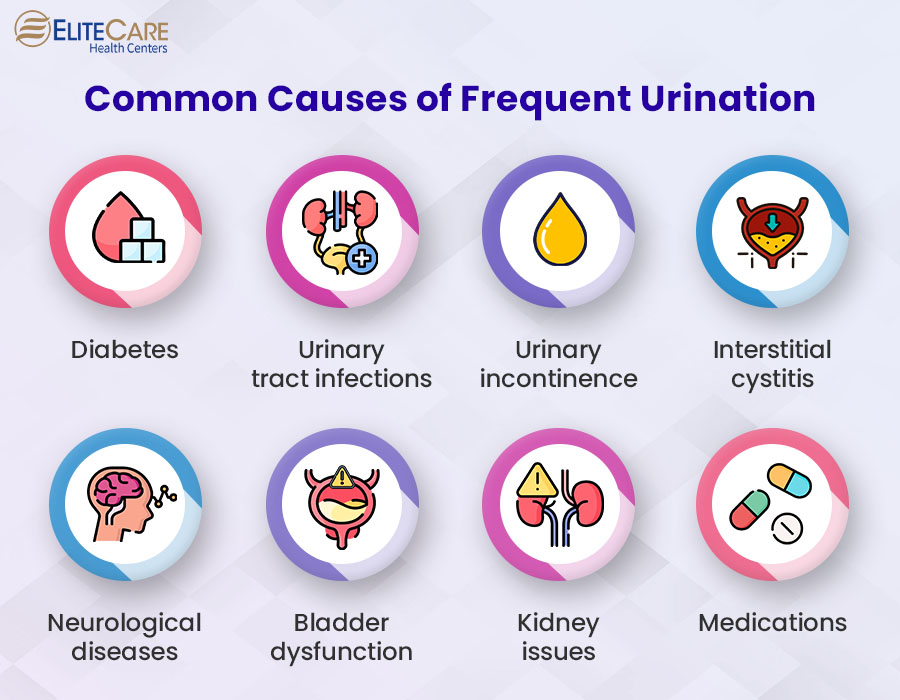
1. Diabetes
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can increase the frequency of urination. As blood sugar levels rise, it can cause the kidneys to filter excess sugar into urine. This additional sugar pulls more water from the body, increasing the amount of urine the body produces.
2. Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Infections in the bladder or urethra can irritate the lining of the urinary tract, increasing urination frequency with burning sensation and discomfort.
3. Urinary incontinence
Loss of bladder control or urinary incontinence can cause involuntary leakage of urine.
4. Interstitial cystitis
Also known as painful bladder syndrome, interstitial cystitis is a chronic condition where the bladder wall becomes inflamed and irritated. As a result, it often leads to an urgent need to urinate even when the bladder is not full.
5. Neurological diseases
Certain neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, stroke, etc., can disrupt the communication between the brain and the bladder and impair bladder control.
6. Bladder dysfunction
One of the most common bladder dysfunctions is overactive bladder, where individuals can feel a sudden, uncontrollable urge to urinate. In addition, bladder cancer can also lead to frequent urination, especially in advanced stages.
7. Kidney issues
Kidney stones, infections, or other kidney diseases can affect how well the kidneys filter and regulate fluids and change urinary patterns, sometimes resulting in frequent urination.
8. Medications
Diuretics are medications prescribed to increase urine production. They can lead to frequent urination as a side effect.
9. Prostate issues
In men, prostate problems like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), enlarged prostate, or prostate cancer can obstruct the urethra and lead to urinary symptoms, including frequent urination.
10. Weak pelvic floor muscles
Women with weakened pelvic floor muscles may experience urinary frequency.
What Causes Frequent Urination at Night
Waking up at night to urinate is considered normal. But waking up too often (four to five times) may indicate other health conditions. Also known as nocturia, this condition may indicate several health issues, including edema (swelling) in the legs, sleep disorders, or even heart disease. Contact a medical clinic or consult a primary care physician immediately for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What Are the Symptoms of Frequent Urination?
Frequent urination itself is a symptom, but it can come with additional signs and symptoms, depending on the underlying cause.
- An intense and sudden urge to urinate
- Pain or discomfort while urinating, indicating conditions like urinary tract infections or interstitial cystitis.
- A burning or stinging sensation during urination commonly associated with urinary tract infections.
- Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can be a sign of various urinary tract conditions, including infections or bladder issues.
- Difficulty initiating urination can occur due to prostate problems in men or pelvic floor issues in women.
- Feeling like the bladder is not completely empty after urinating is often associated with conditions like an enlarged prostate or weak pelvic floor muscles.
- Frequent urination at night.
- Loss of bladder control if it is a case of urinary incontinence.
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia) after urination, especially in cases of diabetes.
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic region can indicate conditions like interstitial cystitis.
- Changes in the color or odor of urine can occur due to certain medical conditions, including dehydration or kidney problems.
Individuals experiencing frequent urination along with any of these additional symptoms should seek medical evaluation to determine the cause.
How to Treat and Manage Frequent Urination
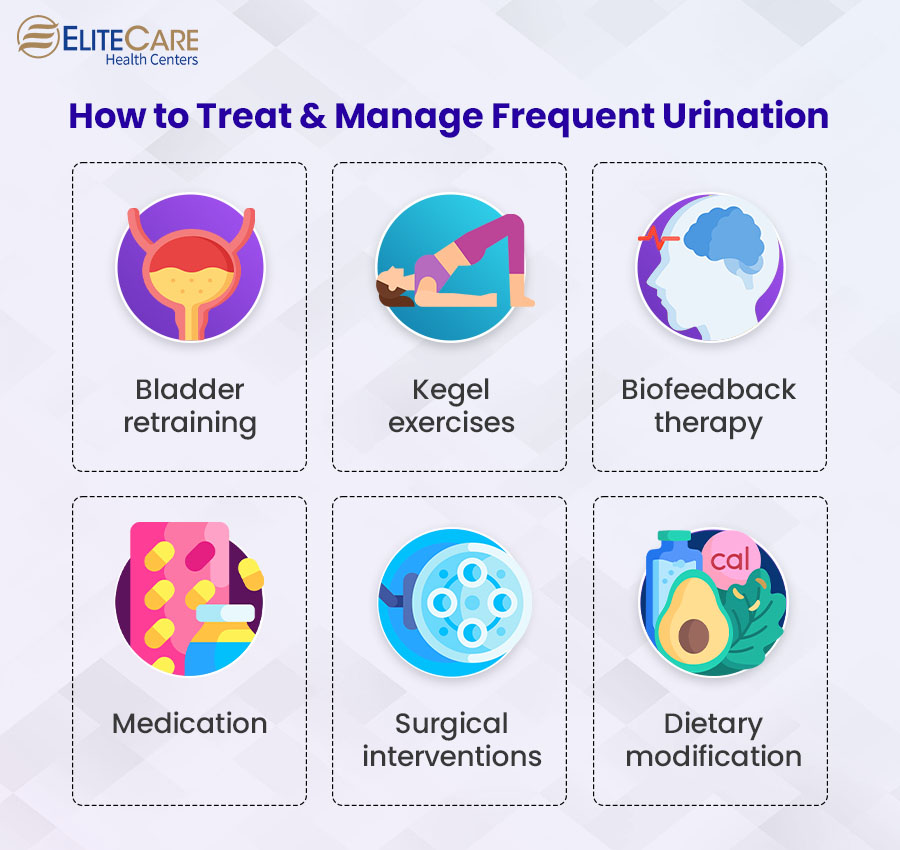
Healthcare providers usually start the treatment procedure by determining the cause of frequent urination. Treatment options for frequent urination can vary depending on the underlying cause. The following are some common treatment approaches:
1. Bladder retraining
It is a behavioral therapy technique that increases the bladder’s capacity and reduces the frequency of urination. This method helps the bladder to hold more urine over time by gradually increasing the intervals between bathroom trips.
2. Kegel exercises
This type of exercise strengthens pelvic floor muscles to help women experiencing frequent urination due to weak pelvic floor muscles. Strengthening these muscles can improve bladder control and reduce urinary incontinence.
3. Biofeedback therapy
With this therapy, individuals can get real-time feedback on muscle activity in the pelvic region through monitoring devices. Therefore, individuals can learn to control and strengthen their pelvic floor muscles accordingly and improve bladder control.
4. Medication
Primary care physicians or healthcare providers may prescribe specific medication to manage the underlying health issue causing frequent urination. For example, while antibiotics can treat urinary tract infections, medicines like anticholinergics or beta-3 adrenergic agonists can control overactive bladder.
5. Surgical interventions
If the primary cause of frequent urination is an enlarged prostate or urinary tract obstruction, providers may consider surgical procedures to treat the problem.
6. Dietary modification
Primary care physicians may also recommend dietary modifications, such as avoiding spicy foods or acidic beverages, which can irritate the bladder and worsen the condition. Additionally, individuals should avoid caffeine and alcohol and limit fluid intake close to bedtime.
The choice of treatment for frequent urination largely depends on the specific diagnosis. Visit a healthcare center and consult a medical professional for a proper evaluation and personalized treatment plan tailored to the underlying cause.
When Should You See a Doctor for Frequent Urination?
When it comes to urinary habits, there’s no one-size-fits-all rule for how often one should urinate in a day. On average, people typically urinate around six or seven times within a 24-hour period. However, this frequency can vary significantly among individuals, influenced by factors such as fluid intake, age, bladder size, and overall health.
Individuals should report any noticeable and persistent change in their urinary habits, especially if it is causing discomfort or producing additional symptoms like pain, blood in the urine, or fever. Such changes may indicate an underlying health condition that needs to be evaluated and treated by a healthcare professional.
For any queries or concerns about frequent urination, bladder control, urinary incontinence, etc., contact EliteCare Health Center, one of the best medical clinics in Florida. We offer a wide range of primary and senior care services, including routine physical exams, preventive screenings, vaccination, etc. Contact us to schedule an appointment with our board-certified primary care physicians at your nearest EliteCare healthcare center.