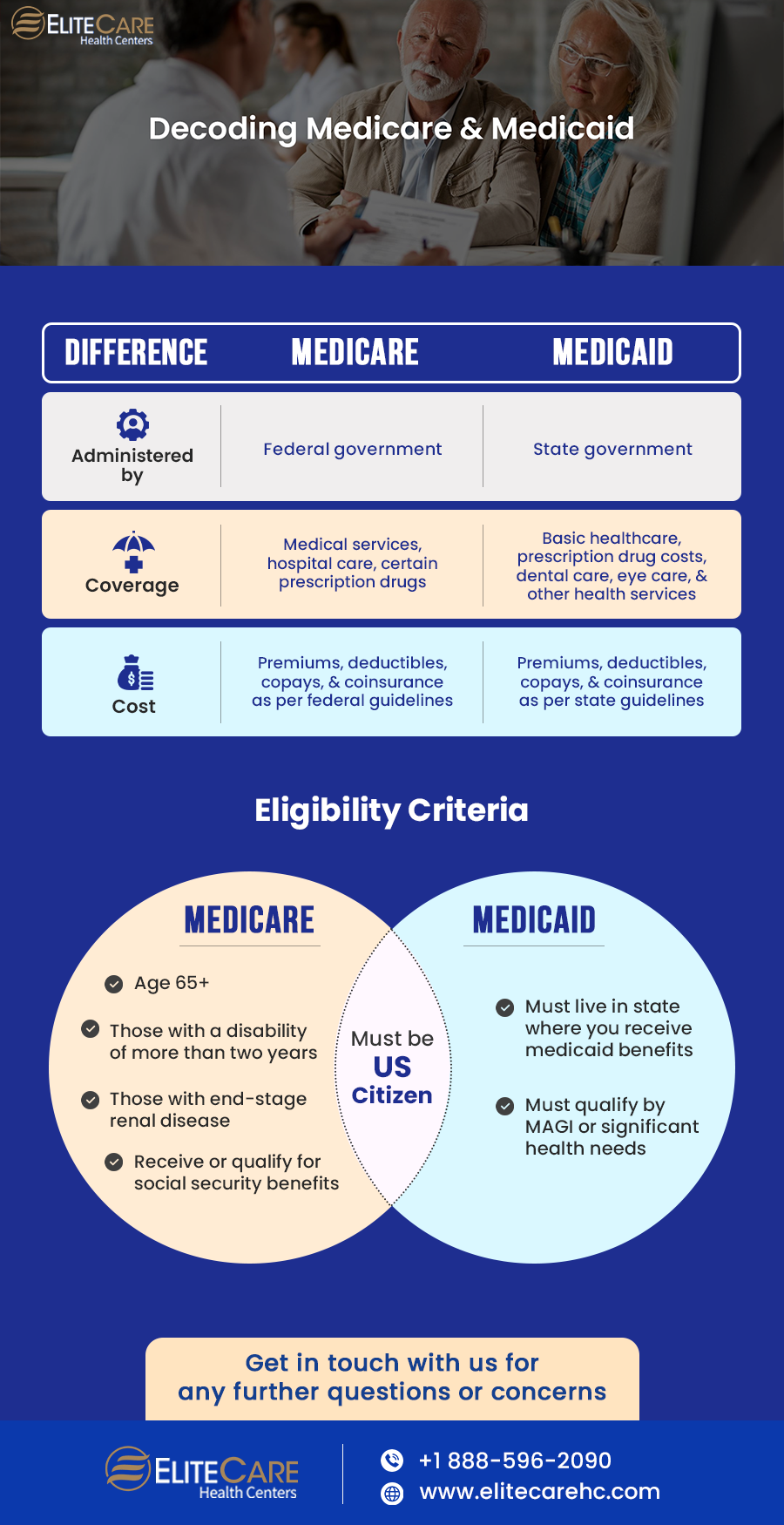
Government-sponsored programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, are intended to help citizens of America with the cost of healthcare. Medicare and Medicaid are federally run healthcare programs that were established in 1965. They are operated and funded by different government agencies and serve different groups.
Medicare is a federal health insurance program and Medicaid is a state and federal joint health insurance program.
The advantages of Medicare and Medicaid go beyond just assisting you to pay for your primary care center services. With similar-sounding names and taxpayer funding, these two programs are often confused as to how they work and what they cover. Let’s discuss the differences between the two.
What is Medicare?
Medicare is a national health insurance program that is available to those 65 years and older, certain categories of disabled persons under the age of 65, and those with end-stage renal disease. Medicare benefits are divided into four components – A, B, C, and D.
Part A – Hospitalizations and other in-patient care are covered in Part A. You can receive Part A benefits directly from the government or by signing up for a
Part B – Doctor visits, outpatient surgery, lab fees, and medical supplies are all covered in Part B. You can receive Part B benefits directly from the government or by signing up for a Medicare Advantage plan..
Part C – It is often known as Medicare Advantage, a privatized version of Medicare that is provided by private insurance companies. Medicare Advantage combines the benefits of Parts A and B with additional benefits, such as prescription drug coverage, dental and vision insurance, and wellness incentives.
Part D – Only commercial insurance providers provide Part D, which covers prescription pharmaceuticals; they do so either through Medicare Advantage plans that also provide prescription drug coverage or through Prescription Drug Plans, which provide Part D coverage separately.
What is Medicaid?
Medicaid is a federal program that provides health insurance coverage to low-income families, including children, pregnant women, seniors, and people with disabilities. It is funded jointly by the federal government and the states.
Each state runs its own Medicaid program in accordance with federal regulations. The broad federal rules provide states with a substantial amount of flexibility in creating and implementing their programs. Medicaid eligibility and benefits as a result can and often do differ greatly from state to state.
Because Medicaid is an “entitlement” program, anyone who meets the qualifying requirements is entitled to sign up for coverage. The Medicaid program is managed by each state independently, so eligibility differs from state to state. You can find out if you qualify by contacting your state Medicaid agency. Alternatively, you can check your eligibility online by visiting the website of your state’s Medicaid agency.
Read more: Myth vs Fact: Can I Get Medicare if I’ve Never Worked?
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
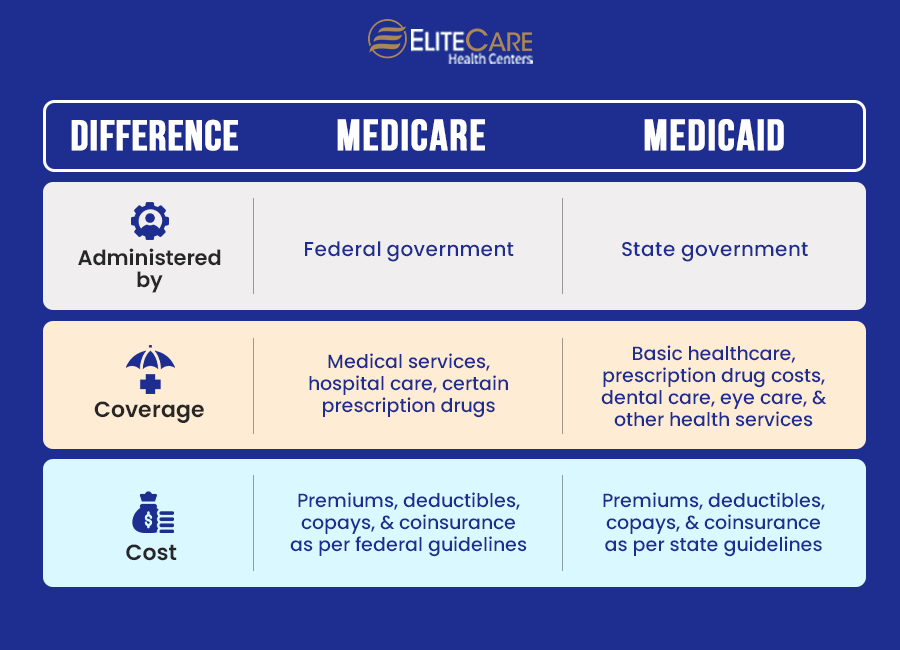
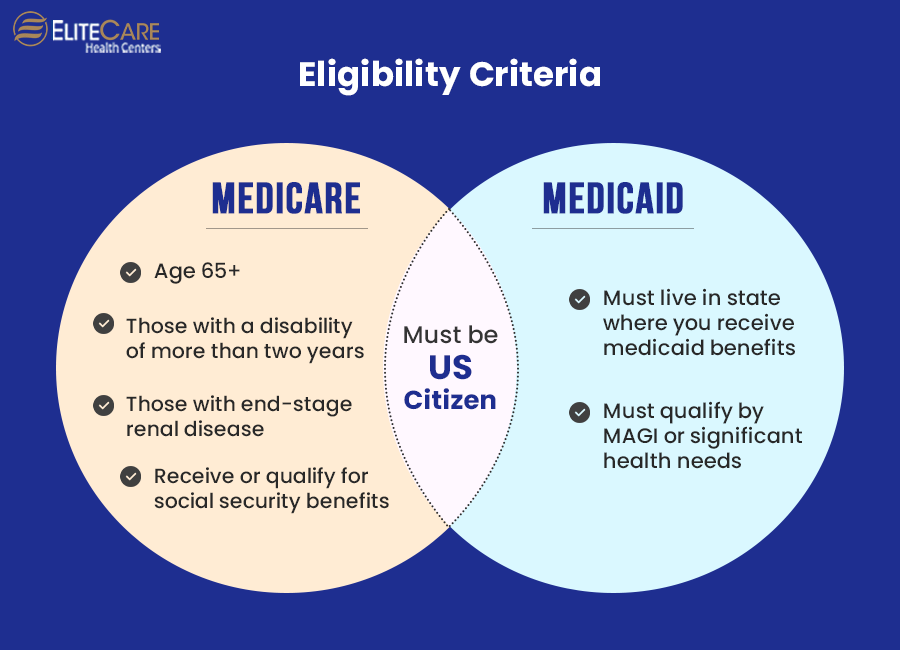
Medicaid and Medicare differ in that Medicaid is governed by the states and is based on income levels. Medicare is primarily based on age under federal supervision. However, in other cases, such as with certain disabilities, younger people may be eligible for Medicare.
Some individuals may qualify for Medicaid and Medicare both owing to their age and the eligibility rule of Medicaid in their state. A person may be eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare based on his or her age and state Medicaid eligibility rules. Due to their eligibility for both Medicaid and Medicare, these individuals are considered “dual eligible.”
Those with both Medicaid and Medicare are the only ones for whom dual health insurance is intended. They fall under the category of Part C (Medicare Advantage) plans, which are unique. Hospital, medical, and prescription drug coverage are all included in dual health insurance. All your Medicaid benefits will be retained. Additionally, you can receive additional benefits compared to Original Medicare.
There are premiums, deductibles, copays, and coinsurance for both Medicare and Medicaid. When you join Medicare, the coverage options you choose, and the medical services and supplies you utilize over the course of the year will all affect how much you pay. Your income and the Medicaid eligibility requirements in your state will determine how much you will have to pay (if at all).
We advise getting in touch with an expert if you have any more questions or concerns or would like more detailed information about Medicare and Medicaid.
- Tags:best primary doctors near meCenter For Wellnesscommon health problems in elderlyhealth and wellness centerhealth and wellness servicesmedical clinicMedicare advantagesmedicare benefitsprimary care centerprimary care physicianprimary care physicians of floridasenior care serviceswellness care centerswellness check doctor