Bone marrow biopsy is a medical procedure used for collecting and examining bone marrow – the soft and spongy tissue found inside some of the larger bones in the body. This procedure provides valuable information about bone marrow health and its ability to produce adequate blood cells. Bone marrow biopsy procedures can help diagnose and monitor various blood and marrow diseases.
What is the Purpose of a Bone Marrow Biopsy?
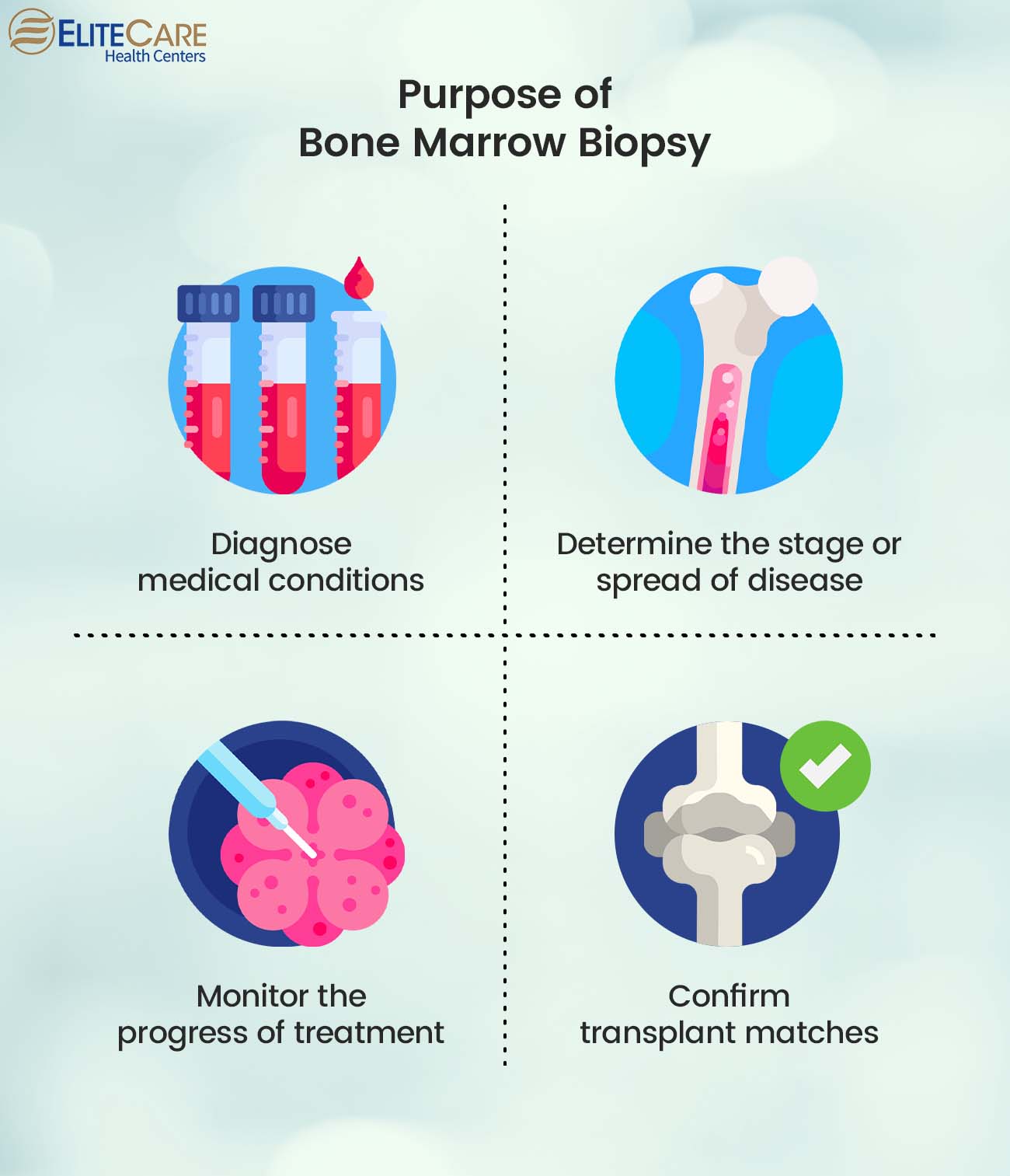
A bone marrow biopsy can provide in-depth insights into the bone marrow and blood cells. The following are some of the primary reasons why primary care physicians may order this test:
1. Evaluate or diagnose medical conditions
If a healthcare provider observes an unusual blood cell count in a blood sample and suspects any health issue, they may request a bone marrow biopsy to confirm a diagnosis.
A bone marrow examination can diagnose various medical conditions, including:
- Anemia
- Disorders involving the production of too few or too many specific types of blood cells, such as leukopenia, leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis, pancytopenia, and polycythemia
- Blood or bone marrow cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma
- Cancers that have metastasized to the bone marrow from other regions, like the breast
- Hemochromatosis
- Unexplained fevers
2. Determine the stage or progression of the disease
This biopsy is one of the main tests to confirm a cancer diagnosis and determine the extent of cancer progression. It can suggest whether cancer has infiltrated the bone marrow or if a tumor within the marrow is growing.
3. Monitor the progress of treatment
Periodic bone marrow biopsy procedures can help healthcare providers monitor the effectiveness of treatment, especially in the case of cancers.
4. Check matches for transplants
In some cases, individuals with insufficient healthy blood cells may require healthy stem cells from a compatible donor. A bone marrow biopsy can confirm whether a donor is a suitable match for an allogeneic stem cell transplant.
Before the Bone Marrow Biopsy Test
Before the procedure, primary care physicians inform individuals about the test in detail, including its potential risks. Physicians may check the following aspects:
- Any pre-existing conditions and medications, over-the-counter treatments, or supplements individuals may be using.
- Family history, with a specific focus on any instances of bleeding disorders.
- Any allergies one may have, including allergies to local anesthetics or latex.
What Happens During a Bone Marrow Biopsy Procedure
For individuals receiving IV sedation, lab technicians will place an intravenous line. Those who are anxious about the procedure may receive oral sedation. Before beginning the test, a hematologist checks the vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature.
In the procedure room, individuals have to lie on their side, back, or abdomen, depending on the biopsy site. There are three sites where the providers perform the bone marrow biopsy procedures, including:
- A hip biopsy is the most common type of bone marrow biopsy and involves two procedures: aspiration and biopsy. Healthcare professionals typically use the back of the hip (posterior iliac crest) to perform this procedure.
- A breastbone (sternum) biopsy is rarely performed due to the risk of severe side effects, such as accidental pericardial perforation.
- A tibia (shin) biopsy is limited to children or infants under age 2, as it provides an insufficient sample in adults.
After determining the biopsy site, healthcare providers perform the following steps:

Step 1
A hematologist or lab technician cleans and drapes the selected biopsy site with sterile towels. Then, they administer local anesthesia that causes a temporary stinging sensation, after which the skin will become numb.
Step 2
Following the anesthesia, they make a small incision in the biopsy site and insert a hollow needle. Individuals will feel pressure as it enters the skin, followed by a sharp, momentary sting as it enters the bone. This needle includes an internal rod called a bone trocar, which the healthcare provider removes after insertion
Step 3
First, the healthcare providers perform the aspiration process. They attach a syringe to the needle, remove the trocar, and withdraw fluid. If this sample lacks sufficient fluid, they may choose another site for additional sampling.
Step 4
Then, they perform the bone marrow biopsy by inserting a thicker needle into the bone with a twisting motion to obtain a core, solid sample of bone marrow. This part of the procedure often causes sharp pain for a brief period during the sample collection.
Once the procedure is complete, healthcare providers remove the needle and apply pressure to the site to stop bleeding. After that, they usually recommend an antiseptic dressing and ask the patient to rest for at least 10 to 15 minutes before leaving.
This procedure usually takes 30 to 40 minutes and does not require a hospital stay. Individuals should strictly follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding recovery. They may instruct you to avoid strenuous physical activity and keep the wound dry for at least 24 hours.
Is Bone Marrow Biopsy Painful?
During the bone marrow aspiration, individuals may experience a sharp, momentary sting, while the core biopsy process may cause brief, mild discomfort. Since numbing the bone is not possible, individuals may also feel pressure, pushing, and pulling sensations, which can be uncomfortable. If there are any concerns about severe pain or discomfort, consult the healthcare provider.
What Does a Bone Marrow Biopsy Report Suggest?
The test results can suggest various medical conditions by assessing factors like cellularity, cell types, cell morphology, atypia, infection or inflammation, fibrosis, metastasis, iron stores, etc. Abnormalities in the report may indicate the presence of several underlying health issues. A healthcare provider analyzes the test results and may request additional examinations if required and confirm a diagnosis.
There are some limitations to this biopsy method. Firstly, the choice of the biopsy site is important because the contents of bone marrow can differ in various parts of the body. A biopsy performed at one site may not accurately reflect the entire marrow and miss localized areas affected by tumors or other conditions.
Consult a Doctor
The most common side effect associated with bone marrow biopsy is bleeding. Although it is relatively rare, affecting fewer than 1% of cases, the risk increases when an individual has a low platelet count.
In addition to bleeding, the following are a few other potential risks of bone marrow biopsy:
- Individuals with a lower count of infection-fighting white blood cells may develop infection.
- Some individuals may experience persistent pain at the bone marrow biopsy site.
- In the case of the breastbone (sternum) biopsy, there is a slight risk of damage to nearby structures due to its proximity to the heart and lungs.
Individuals should consult a primary care physician immediately if they notice any of the following signs after a bone marrow biopsy:
- Severe bleeding or continuous drainage from the biopsy site
- Redness and swelling at the biopsy site
- Fever and chills with soreness
- Persistent, severe pain
For any further queries or concerns, contact EliteCare Health Centers, one of the best medical clinics and health and wellness centers in Florida, and consult our board-certified primary care physicians. We have multiple healthcare centers across Florida, offering personalized primary and senior care services, including venipuncture, diagnostic tests, and screenings, vaccination, routine physical exams, etc. Schedule an appointment with your nearest EliteCare Health Centers center now!