Through the removal of waste and extra fluid, the urinary system is essential to the body’s overall health maintenance. It is not immune to different problems, though, which can impact people of all ages and socioeconomic backgrounds.
Understanding the Urinary Tract
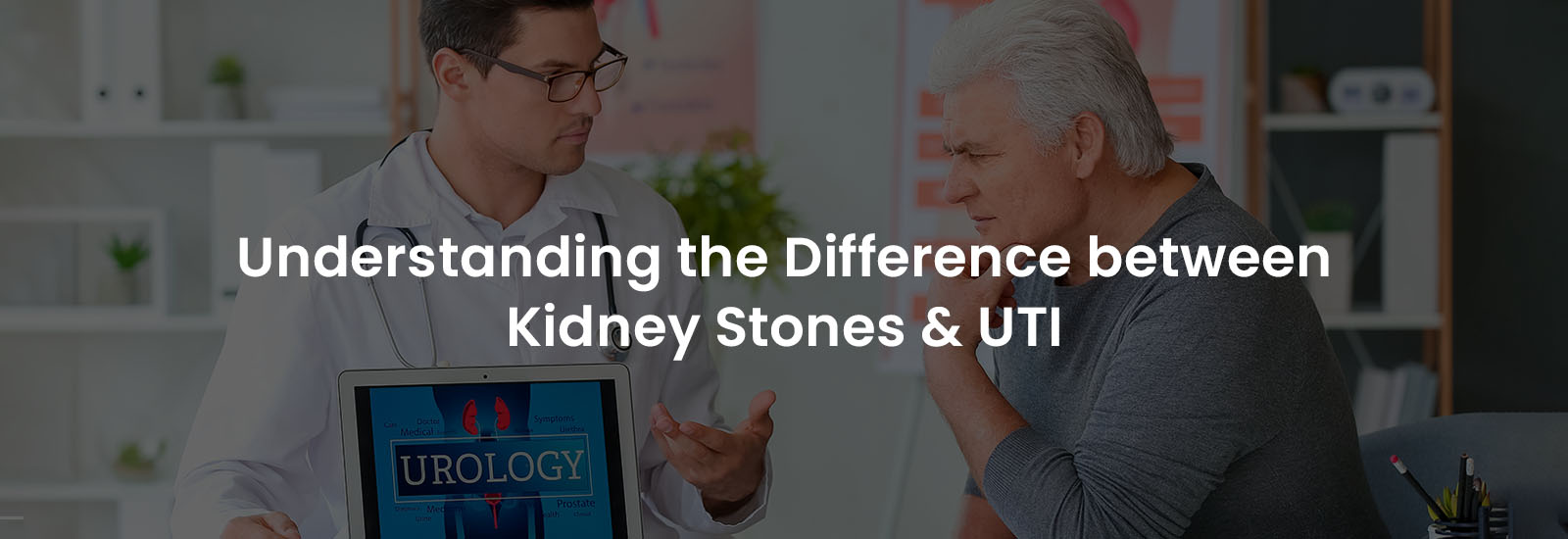
The urinary tract is made up of kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Every element has a distinct function in the production and removal of urine.
- Kidneys: These bean-shaped organs filter waste and excess fluids from the blood to produce urine.
- Ureters: These tubes transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: A muscular organ that stores urine until it’s ready to be expelled.
- Urethra: A tube connecting the bladder to the external body, allowing urine to exit.
Urinary Tract Infections
Among the most common problems with the urinary system are urinary tract infections. They develop when bacterial germs enter the urinary tract and trigger an infection. Since women’s urethras are smaller than those of men, bacteria are more likely to enter the bladder, increasing the risk of urinary tract infections.
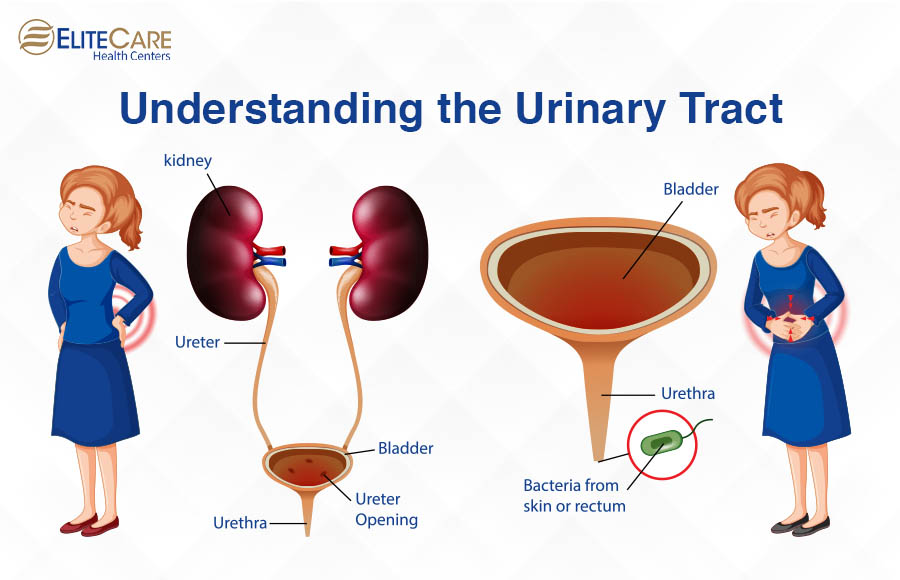
Causes:
- Bacterial invasion, commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli).
- Use of certain contraceptives.
- Urinary tract abnormalities.
- Weakened immune system.
Symptoms:
- Pain or burning sensation during urination.
- A frequent urge to urinate.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
- Lower abdominal pain.
- Fever and fatigue in severe cases.
Treatment:
Based on your bacterial infection, your primary care provider will prescribe certain antibiotics and pain relievers as part of your treatment plan. Your doctor may also increase your fluid intake to flush out the bacteria.
Staying hydrated, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding using irritating feminine products are good preventative measures
Kidney Stones
Solid masses known as kidney stones develop in the kidneys as a result of crystals separating from urine. The size of these stones varies, and going through the urinary tract may hurt a great deal.
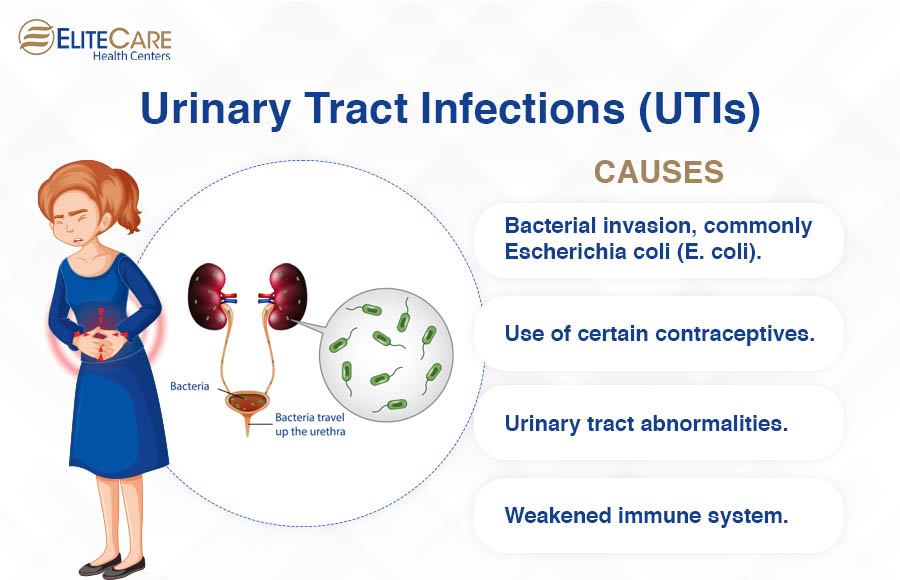
Causes:
- Dehydration.
- High levels of certain minerals in the urine.
- Family history.
- Obesity.
Symptoms:
- Severe back pain.
- Blood in urine.
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Treatment:
Pain medications, increased fluid intake, and in certain cases even surgical intervention for large stones may be suggested by your primary care doctor.
Prevention:
Hydrating yourself, limiting your salt and protein intake, and maintaining are healthy weight play a significant role in prevention.
Bladder Issues: Cystitis and Interstitial Cystitis
Cystitis:
Bladder inflammation, or cystitis, is frequently brought on by a bacterial infection. It is more common in women and can be either acute or chronic.
Bacterial infection, certain contraceptives, and bladder abnormalities are common causes of cystitis.
You may be able to recognize it by symptoms of frequent urination, a burning sensation, lower abdominal pain, and strong-smelling urine.
Urinalysis and urine culture can be done for an accurate diagnosis.
Ensure that you wipe front to back after using the toilet, urinate promptly after sexual activity, and keep yourself hydrated in order to prevent this.
Interstitial Cystitis:
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic condition involving bladder inflammation and irritation. This has a significant impact on a person’s quality of life.
Causes:
- Unknown, but may involve a defective bladder lining.
- Autoimmune reactions.
- Genetic factors.
Symptoms:
- Chronic pelvic pain.
- Urgency and frequency of urination.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Painful urination.
Treatment:
Preventative medications to reduce inflammation, bladder distension, and physical therapy are recommended treatment plans. You should avoid food and drink triggers. Consider taking up stress management techniques and pelvic floor exercises as well.
Incontinence
The uncontrollable leaking of urine is a characteristic of urinary incontinence. It might vary from sporadic minor leaks to a total lack of control over one’s bladder.
All ages and genders are susceptible to this illness, albeit older folks are more likely to experience it.
Causes:
- Weak pelvic floor muscles.
- Nerve damage.
- Hormonal changes.
- Certain medications.
- Urinary tract infections.
Symptoms:
- Unintentional urine leakage.
- Sudden, intense urge to urinate.
- Frequent urination.
Treatment:
Usual treatment plans include pelvic floor exercises (Kegels), prescription drugs, bladder training, and even surgical intervention in certain cases.
Urinary Retention
Urinary retention can occur suddenly or in stages. While chronic urine retention happens gradually over time, acute urine retention is a medical issue that needs to be treated right once. Both medical conditions are susceptible to a variety of underlying causes, and effective management requires an awareness of these aspects.
Causes:
- Enlarged prostate in men.
- Nerve damage.
- Urinary tract obstruction.
- Medications.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty initiating urination.
- Weak urine stream.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- The feeling of incomplete emptying.
Treatment:
Primary care doctors may suggest catheterization to empty the bladder and prescribe medications to relax the bladder muscles.
Prompt treatment of underlying conditions is extremely necessary which is why regular medical check-ups should not be neglected.
Maintaining a healthy urinary tract is extremely important for overall well-being. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of common urinary tract issues is the first step toward timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
EliteCare HC is home to some of the best primary care physicians in Florida. For any concerns related to UTIs, contact us via our website or book an appointment by calling +1 888-596-2090.
- Tags:bladder infection vs kidney stoneselite healthcarekidney stone or urinary tract infectionkidney stone vs utikidney stones vs utimedical clinicprimary care servicesUrinary Problemsurinary tract infection vs kidney stonesUrinary Tract Infectionsuti or kidney stoneuti versus kidney stonesuti vs kidney stone
Frequently Asked Questions
UTIs, blood in urine, cystitis, and urinary retention are common urinary tract issues.
Common UTI causes include dehydration, constipation, and uncontrolled diabetes.
Urgency to pee constantly, blood in urine, and even pain in your lower side are common symptoms of a UTI.