
Nosebleeds or epistaxis occur when blood vessels within the delicate lining of the nose rupture and bleed. The prevalence of nosebleeds is fairly common, with about 60% of people reporting at least one nosebleed in their lifetime.
Nosebleeds can be of two types: anterior nosebleeds, which begin in the blood vessels at the front of the nose, and posterior nosebleeds, which originate from deeper vessels at the back of the nose. Anterior nosebleeds are more common and less severe, while posterior nosebleeds are less common and more concerning since they may involve larger blood vessels.
In this blog post, we will share detailed insights into nosebleed causes, prevention, and how to stop nosebleeds quickly at home. Read on for more.
Causes of Nosebleeds
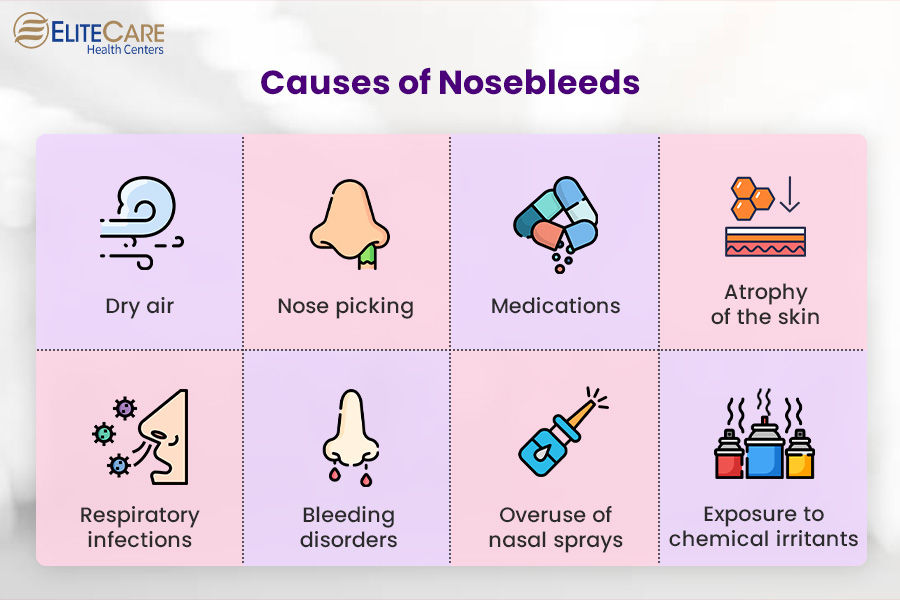
Nosebleeds among seniors can result from a combination of age-related factors, underlying health issues, and environmental factors, which are as follows:
1. Dry air
As we age, we tend to lose moisture in the nasal passages, making the blood vessels more susceptible to breaking. Dry air, whether from indoor heating systems or arid climates, can exacerbate this issue and result in nosebleeds.
2. Nose picking
Be it children, adults, or seniors – picking a nose can lead to nosebleeds in anyone. However, as the skin lining the nose becomes thinner with age, seniors become more susceptible to nosebleeds even in case of minor traumas.
3. Medications
Seniors often take multiple medications, some of which may have blood-thinning components. Blood thinners or antiplatelet drugs, including aspirin, can prevent clotting and increase the risk of nosebleeds in seniors.
4. Atrophy of the skin
It refers to the thinning and weakening of the skin’s structure over time, mostly due to aging. As the skin naturally loses its elasticity with age, the blood vessels within the nasal lining become more fragile, making them more prone to rupture.
5. Respiratory infections
Seniors are more susceptible to respiratory issues, which can lead to inflammation, increased nasal congestion, swelling of blood vessels, and irritation of the nasal passages. Respiratory conditions like sinusitis, common cold, etc., can create an environment where blood vessels are more likely to break, resulting in nosebleeds.
6. Bleeding disorders
While relatively uncommon, seniors may develop bleeding disorders due to age-related changes in their body’s clotting mechanisms. These disorders can increase the frequency and severity of nosebleeds.
7. Overuse of nasal sprays
Frequent use of nasal sprays, especially those containing decongestants, can lead to irritation and dryness of the nasal passages.
8. Exposure to chemical irritants
Seniors are more sensitive to chemical irritants like strong cleaning agents, harsh fumes from paints or solvents, and environmental pollutants. These irritants can trigger nosebleeds in individuals with compromised nasal linings.
The following are a few other factors and health conditions which may also cause nosebleeds:
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- High blood pressure
- Facial and nasal surgery
- Nasal tumors or polyps
- Immune thrombocytopenia
- Cancer
In order to find out the definite causes of nosebleeds in seniors, it is crucial to visit a healthcare center and consult a primary care physician.
How to Prevent Nosebleeds in Seniors

1. Buy a humidifier
Using a humidifier in indoor spaces can help maintain optimal humidity levels, preventing the nasal passages from drying too much.
2. Use saline nasal spray
If a senior suffers from a dry nose, using saline nasal sprays can help keep the nasal passages moisturized and soothe irritation.
3. Avoid nose picking
Seniors should resist the urge to pick their noses, especially those with thinner nasal linings.
4. Apply water-soluble nasal gels
This type of nasal gel or ointment can provide a protective barrier, preventing the nasal lining from drying out and minimizing the risk of bleeding.
5. Sneeze with an open mouth
When sneezing, seniors should keep their mouths open to alleviate pressure within the nasal passages. It will reduce the risk of rupturing the blood vessels. Always use the elbow or a napkin while sneezing.
6. Manage medication
Seniors taking multiple medications, especially blood thinners, should consult their primary care physician about the potential impacts of their medicines on clotting and discuss alternative options if required.
7. Stay hydrated
Drinking enough water helps maintain general hydration levels, which can also prevent the nasal passages from drying out.
8. Quit smoking
Seniors who smoke should try quitting because smoking can exacerbate dry nose and trigger inflammation.
9. Protect from irritants
Minimize exposure to chemical irritants by using masks and maintaining hygiene.
How to Stop Nosebleeds
Seniors and caregivers can use the following steps to stop or control a nosebleed at home:
- Sit in an upright position and tilt your head slightly forward. Avoid lying flat or bending your head between your legs. This prevents blood from flowing down your throat, which could lead to nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- Breathe through your mouth to maintain a clear airway.
- Gently pinch the soft part of your nose using your thumb and index finger. Make sure to apply pressure against the hard bony ridge that forms the bridge of your nose. Pressing higher up won’t effectively stop the bleeding.
- Continue pinching your nose for a continuous five minutes before checking if the bleeding has ceased. If bleeding persists, keep applying pressure for an additional 10 minutes.
- Additionally, apply an ice pack to the bridge of your nose to narrow blood vessels, which can slow down the bleeding. While not mandatory, seniors can try it to relieve any discomfort.
- If needed, you can use an over-the-counter decongestant spray like oxymetazoline on the bleeding side of your nose. Remember, these sprays should not be used for an extended period, as they can increase the likelihood of irritation.
- Once the bleeding has stopped, avoid bending over, straining, or lifting heavy objects. Refrain from blowing or rubbing your nose for several days.
If the nosebleed persists despite these measures or becomes a recurrent issue, consult a primary care physician to rule out any underlying concerns.
When to See a Doctor
While most nosebleeds are easily manageable at home, certain situations require a visit to a medical clinic. Consult a primary care physician in the following situations:
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Bleeding persisting for 20 minutes or more even after applying direct pressure
- Severe bleeding following an injury
- Breathing difficulties
In case of significant or persistent blood loss, call 911 directly for immediate medical attention.
For any queries or concerns about nosebleeds, contact EliteCare Health Centers, one of the best medical clinics in Florida that offers comprehensive senior care services. Contact us and schedule an appointment with our board-certified primary care physician.






