As we age, prioritizing our health and well-being becomes increasingly important to us. One simple and readily available beverage that can contribute significantly to overall health is milk. In this blog post, we will share the nutritional benefits of milk, recommended daily intake, and how milk benefits seniors. Read on to learn more.
Nutritional Values of Milk
Protein
The protein content in a glass of milk may vary depending on the type of milk (whole, skim, low-fat, etc.) and the serving size. However, on average, a typical 8-ounce (240 ml) glass of cow’s milk contains about 8 grams of protein. The protein in milk is of high quality and provides all the essential amino acids necessary for the growth and repair of body tissues.
Fat
The amount of fat content present in milk may also vary depending on the type of milk one is consuming. While whole milk typically contains around 3.7% fat, reduced-fat milk has about 2% fat, and skim milk contains no fat.
Carbohydrates
An 8-ounce (240 ml) glass of milk typically contains approximately 12 grams of lactose, which works as an energy source and is broken down into glucose and galactose during digestion.
Vitamins
Milk is a good source of various essential vitamins, including vitamin D, vitamin B12, vitamin A, and riboflavin (vitamin B2). The exact percentages can vary depending on the type of milk consumed. However, whole milk typically contains approximately 10-15% of the recommended daily intake for these vitamins.
Read More: Recognizing the Vital Role of Vitamin C in Our Lives
Minerals
Milk also contains several essential minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and potassium. Whole milk typically provides about 28-30% of the recommended daily intake for calcium.
The amount of nutrients in milk may vary largely depending on its type and whether it is fortified. Additionally, milk from different animals (such as goat’s milk or sheep’s milk) may have slightly different nutritional profiles than plant-based milk options.
Health Benefits of Milk for the Elderly
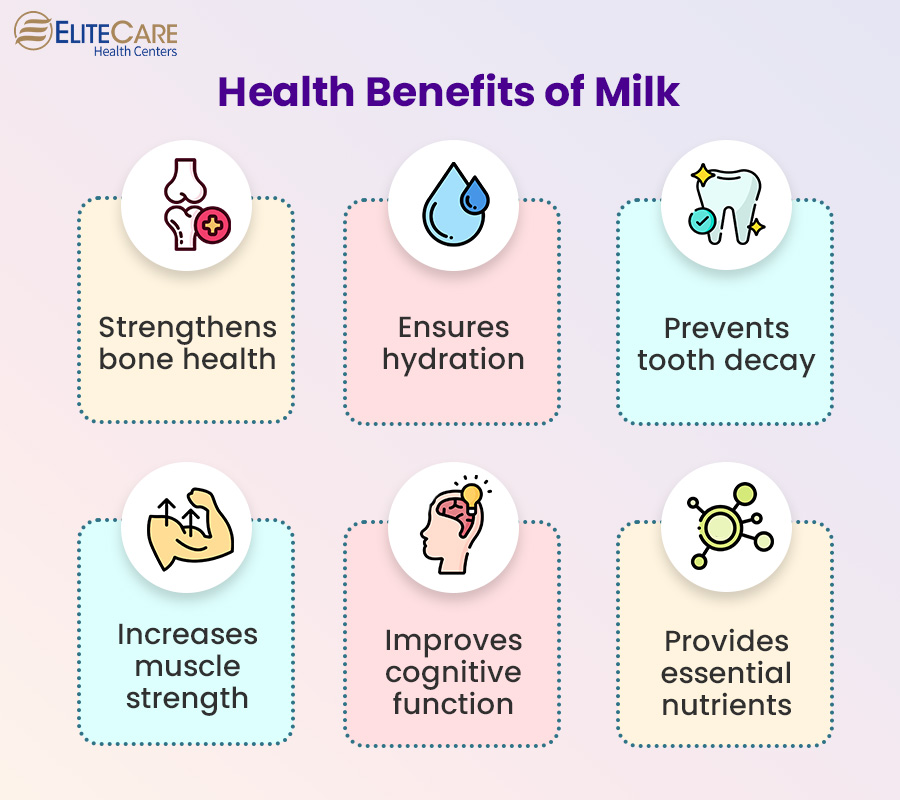
1. Strengthens bone health
Milk is an excellent source of calcium, which is crucial for maintaining strong bones and preventing osteoporosis. Adequate calcium intake with vitamin D can help reduce the risk of fractures and promote bone health in seniors.
2. Increases muscle strength
Protein is essential for maintaining muscle mass and strength, especially in older adults. Milk contains high-quality proteins that can support muscle protein synthesis and help prevent age-related muscle loss or sarcopenia.
3. Provides essential nutrients
Milk is a nutrient-dense beverage, providing several essential vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D, vitamin B12, riboflavin, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients play important roles in overall health, including immune function, nerve health, and energy production.
4. Ensures hydration
Older adults often suffer from dehydration due to various factors such as reduced thirst sensation or medication use. Milk can contribute to daily fluid intake and help maintain proper hydration levels.
5. Improves cognitive function
Some studies suggest that milk consumption along with other dairy products may be associated with better cognitive function in older adults. The presence of nutrients like B vitamins, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids in milk may contribute to brain health.
6. Prevents tooth decay
Milk benefits health by providing calcium and phosphorus- minerals essential for the formation and remineralization of tooth enamel. These minerals help strengthen the teeth and protect them from decay.
In addition, milk also contains casein and whey proteins, which form a protective film on the teeth, helping to prevent the adhesion of harmful bacteria and reducing the risk of tooth decay.
Individual dietary needs may vary, and some older adults may have specific dietary restrictions or lactose intolerance. Therefore, consulting with a primary care physician or a registered dietitian is recommended for personalized advice.
Concerns About Milk Consumption for the Elderly
While milk can provide several health benefits for seniors, there are some challenges and concerns associated with mill consumption, which are as follows:
Lactose intolerance
Many seniors suffer from lactose intolerance, a condition in which the body has difficulty digesting lactose, the natural sugar found in milk. It can cause a number of digestive issues such as bloating and diarrhea when consumed. Seniors with lactose intolerance may need to avoid milk consumption or opt for lactose-free milk. or dairy alternatives like yogurt.
However, researchers have found that lactose-free milk may contain high amounts of sugar which may not be suitable for seniors with diabetes or prediabetes. One glass of lactose-free milk contains approximately 12 grams of sugar. Therefore, it is crucial to read labels and consult a dietitian for detailed guidance.
Allergies
Although rare, some seniors may have milk allergies, which can cause adverse reactions ranging from mild symptoms like hives to severe allergic reactions. Allergies to milk protein require complete avoidance of milk and dairy products.
Calcium and Vitamin D interactions
While milk is a good source of calcium and vitamin D, some medications commonly used by seniors, such as certain diuretics or corticosteroids, can interfere with calcium absorption or vitamin D metabolism. Seniors should consult their healthcare providers about potential interactions and adjust their intake or consider supplements accordingly.
The Daily Recommended Intake of Milk for Seniors
The recommended intake may vary depending on individual dietary needs and health factors. However, general guidelines suggest that older adults aim for 2-3 servings of dairy products including milk, each day. One serving of milk typically refers to 1 cup (8 fluid ounces).
In order to determine the specific daily intake of milk for an individual, it is best to consult a primary care physician or registered dietitian.
Conclusion
Seniors should consider a few factors while buying milk. It is important to examine the nutritional contents of milk products. Additionally, opt for milk with little to zero added sugar to promote a healthier diet for seniors. While considering dairy substitutes, choose products fortified with additional vitamins and minerals. Fortification ensures that seniors can still obtain the essential nutrients typically found in milk, even if they opt for non-dairy alternatives. For any queries or concerns about your diet, contact EliteCare Health Center, one of the best medical clinics in Florida, and consult a board-certified primary care physician.