Digestion is the process through which food is broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by the body for energy and nutrients. But age-related bodily changes can make this process complicated for senior citizens. Slow metabolism, loss of teeth, dry mouth and other such issues can cause digestive problems in the elderly. But before we explore this issue, it is important to first understand how digestion works.
Most people go through this process multiple times a day. In adults who eat a balanced diet and have no underlying health conditions, food digests smoothly without any difficulty. But digestive problems become more prevalent in senior citizens who are 60 and older.
Read More: Finding a Low Sodium Diet for Older Adults
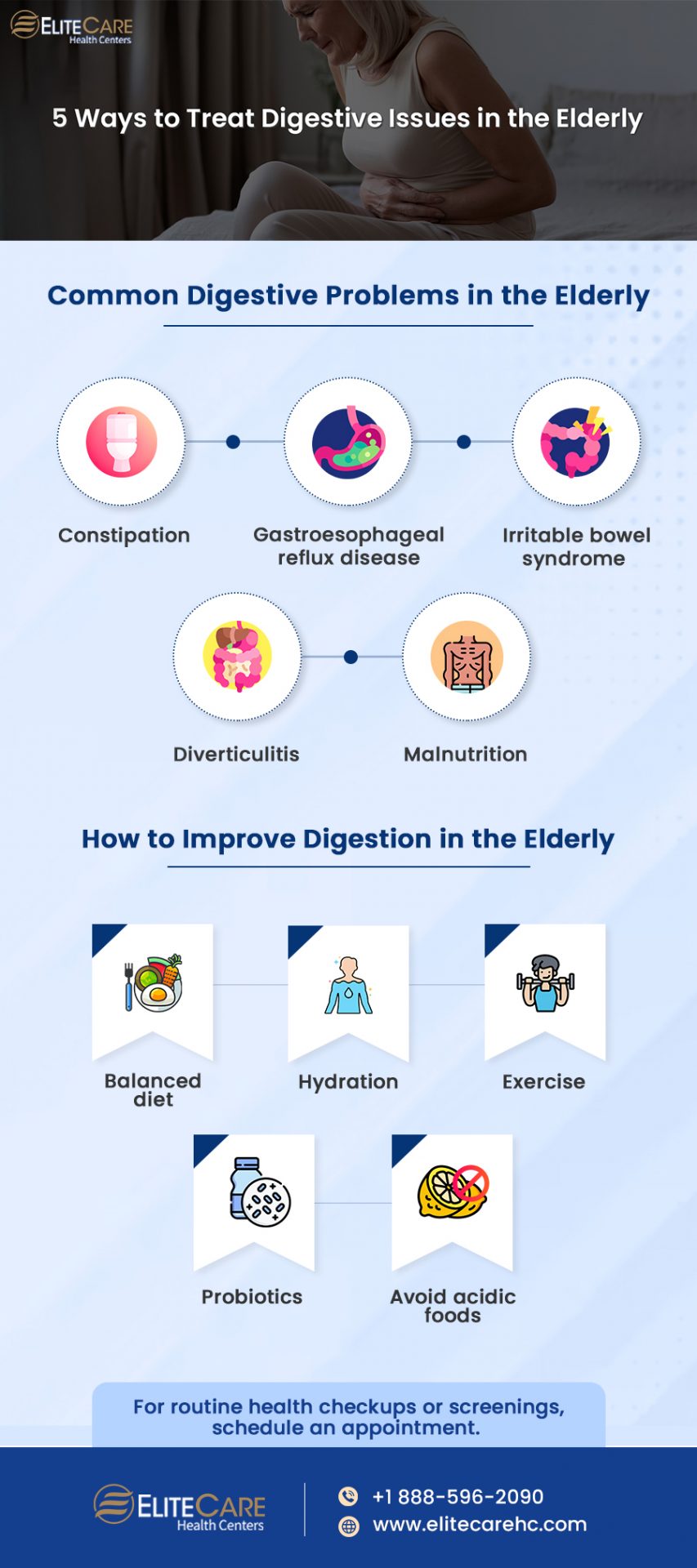
Common Digestive Problems in the Elderly
As people age, their digestive system slows down, which leads to a decrease in the production of digestive enzymes. Without sufficient digestive enzymes, the body cannot break down food into smaller, more absorbable particles. Additionally, aging can affect the stomach’s ability to empty properly, which can lead to bloating. It is also not uncommon for seniors to develop intolerance to certain foods that they previously enjoyed with no digestive problems, such as milk, gluten and foods high in fiber.
Low levels of digestive enzymes, food intolerances and other related problems can increase seniors’ risk of developing certain digestive problems, such as:
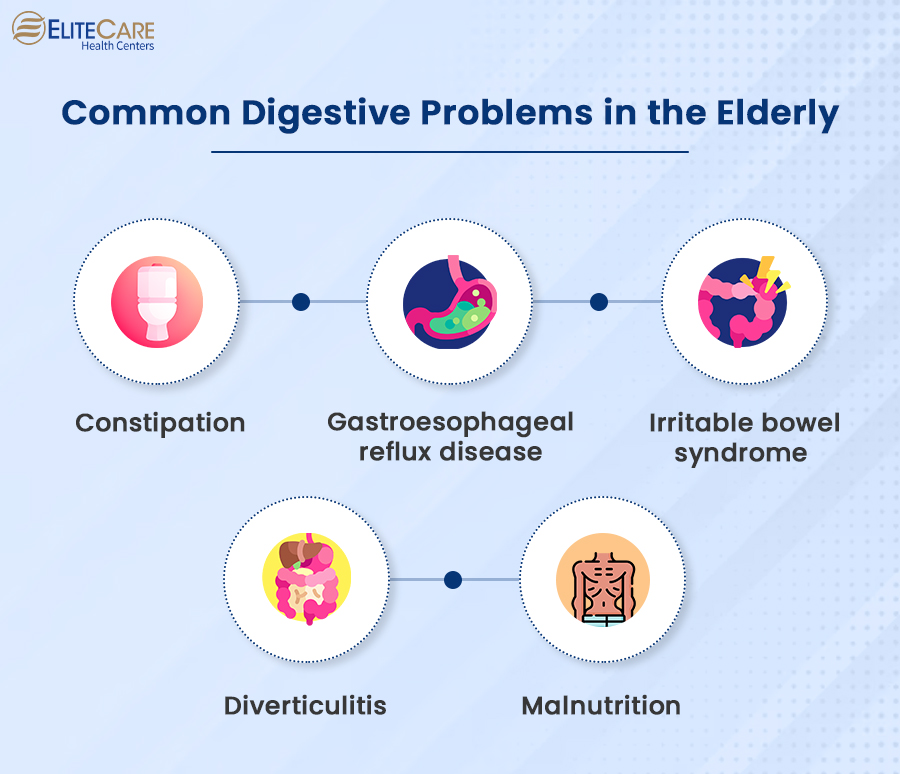
Constipation
Constipation is a common problem that can affect people of all ages, but it is particularly common in the elderly. 26% of women and 16% of men who are 65 or older report suffering from constipation. This is because bowel movements become less frequent as digestion slows down and the muscles in the digestive tract become weaker. Left untreated, constipation can cause serious pain and discomfort in the elderly.
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, also known as GERD, is a digestive disorder where the acids in the stomach travel upwards into the esophagus. This can cause heartburn and regurgitation in the elderly. GERD, like most other digestive problems, becomes more prevalent as people age. About 20% of senior citizens report suffering from GERD symptoms.
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a group of symptoms that affects the stomach and intestines. Symptoms of IBS include stomach cramps, diarrhea, constipation, bloating and gas. The exact prevalence of IBS in older adults is not known, but it is estimated that around 20% of seniors who are 60 and older experience these symptoms.
Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a condition that occurs when small pouches in the wall of the intestine, called diverticula, become inflamed or infected. This condition is more common in older adults, particularly those over the age of 60. Seniors suffering from diverticulitis experience abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and bloating.
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is a condition in which the body does not receive enough nutrients to function properly. When clogged arteries reduce blood flow to the intestines, it can make it difficult for the gut walls to absorb the nutrients that are essential for the body. Malnutrition can cause significant weight loss and is associated with increased mortality in seniors.
An aging digestive system can also make seniors susceptible to late-onset food allergies. About 5-10% of seniors report developing food allergies in adulthood. If senior citizens suspect that they are allergic to certain foods, it is best to consult a physician for screening to receive appropriate treatment.
Digestive issues can have a detrimental effect on seniors’ nutrition and overall health. Therefore, they need to take certain steps to prevent problems from becoming worse.
5 Ways to Improve Digestion in the elderly

Here are some preventative measures senior citizens can take to improve their digestion:
Eat a balanced and nutritious diet
Including fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation.
Stay hydrated
Drinking enough water can help relieve constipation and improve the overall functioning of the digestive system.
Exercise regularly
Physical activity can help stimulate the muscles in the digestive tract and improve bowel movements.
Take probiotics
Seniors are recommended to include fermented foods, dairy and meat in their diets to get beneficial probiotic strains like Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus reuteri. They can help improve digestion by restoring the balance of healthy bacteria in the gut.
Avoid foods that trigger symptoms
Seniors must avoid foods that trigger acid reflux or other digestive problems. It helps to keep a diary to track foods that upset the stomach or cause symptoms of allergy.
Seniors who suffer from persistent digestive problems, such as abdominal pain, bloating, or changes in bowel habits should visit a health and wellness center to receive proper medical attention. It’s also important for seniors to talk to their physician about any medications that they are taking, as some of them may have side effects that affect digestion. The doctor may then be able to provide alternative medication that doesn’t cause digestive problems.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that while digestive problems are common among seniors, they are not an inevitable part of aging. By maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle, seniors can reduce their risk of developing digestive problems as they age.
If your elderly loved one needs personalized advice on health and nutrition, visit the nearest EliteCare Health Centers clinic for more help. EliteCare is one of Florida’s best medical clinics, with a team of highly trained primary care physicians who offer services like venipuncture, immunizations, EKG and more. Visit their website to schedule an appointment today.