The treatment for bacterial infections was revolutionized with the invention of antibiotics. But antibiotics are not effective against viral infections, such as the common cold or the flu. Different antibiotics have different effects on bodily functions, but most of them target specific components of bacterial cells and disable their growth and reproduction.
While antibiotics can be highly effective against bacterial infections, the misuse and overuse of antibiotics can cause antibiotic resistance. In this blog post, we will share detailed information on what antibiotic resistance is, why it is a critical medical concern, and what we can do to avoid it. Read on to learn more.
Antibiotic Resistance & Its Causes
Antibiotic resistance refers to the ability of bacteria in the body to resist the effects of antibiotics, making them less effective or completely ineffective against a disease. It can occur due to a number of reasons which are as follows.
1. Genetic mutation
Bacteria can mutate over time and these new strains can survive even in the presence of existing antibiotics. These resistant bacteria can then spread even further, leading to the emergence of more antibiotic-resistant strains.
2. Misuse and overuse of antibiotics
Antibiotic resistance mostly develops due to misuse and overuse of antibiotics. It mostly happens to those who self-medicate. Overuse of antibiotics can kill off both the harmful bacteria causing the infection as well as the beneficial bacteria that reside in the body. As a result, it creates an environment where antibiotic-resistant bacteria have a competitive advantage and can grow further.
Similarly, when antibiotics are misused, such as when they are prescribed for viral infections or when patients do not complete the full course of treatment, it can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance.
3. Agricultural use
The widespread use of antibiotics in agriculture has contributed significantly to antibiotic resistance. Antibiotics used in agriculture, specifically in livestock and poultry production, help prevent infections and promote growth in animals. However, it can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in animals. This resistance can later be transmitted to humans through the food chain.
Consequences of Antibiotic Resistance
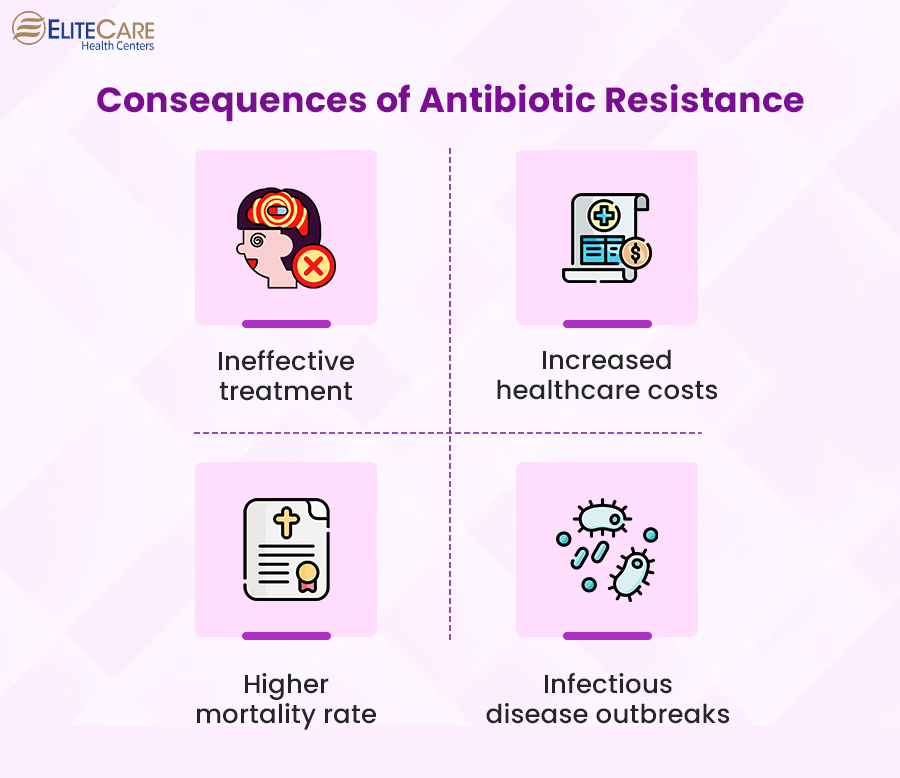
1. Higher morbidity and mortality rate
Antibiotic resistance can increase morbidity and mortality rates because the usual antibiotics don’t work to treat infections. Besides, the infection caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria is more difficult to treat. Therefore, they may require more aggressive treatment options, such as surgery or prolonged hospitalization. In some cases, there may be no effective treatment options available, leading to an increased risk of death.
2. Increased healthcare costs
3. Ineffective treatments
Due to antibiotic resistance, infections that were once easily treatable with antibiotics may now require alternative treatments or may be untreatable altogether since the bacteria become resistant to them.
For example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a bacterial infection that has now become increasingly resistant to multiple antibiotics.
4. Threat of infectious disease outbreaks
Due to the overuse of antibiotics, they are no longer effective against certain bacterial infections. These infections can spread more easily and rapidly, leading to outbreaks in communities, hospitals, and other settings.
In recent years, outbreaks of antibiotic-resistant infections such as Clostridioides difficile and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) have occurred in healthcare facilities.
How to Prevent Antibiotic Resistance

1. Use antibiotics responsibly
Antibiotics should only be used when prescribed by a healthcare professional, as they are trained to determine whether an antibiotic is necessary and which type of antibiotic would be most effective.
2. Complete the full course
Individuals should complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve. It will ensure that all bacteria are eliminated from the body. If individuals stop taking antibiotics prematurely, bacteria may survive and develop resistance to the drug, making it more difficult to treat the same infection in the future.
3. Get vaccinated
Vaccines can help prevent infections that require the use of prescribed antibiotics, such as pneumonia, meningitis, and influenza. By preventing these infections, it is possible to reduce the need for antibiotics and control the development of antibiotic resistance.
4. Use alternative methods to prevent infections
Proper wound care and safe food handling can also help prevent infections that may require antibiotics later on.
5. Reduce the use of antibiotics in agriculture
It is crucial to promote sustainable farming practices instead of using antibiotics to increase production. It can help reduce the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in animals and prevent the spread of these bacteria to humans through the food chain.
Conclusion
Antibiotic resistance can not only make it difficult to treat common infections but can also have a significant impact on medical procedures that rely on effective antibiotic treatment, such as surgeries, cancer treatments, organ transplants, etc. Therefore, we must come together to spread awareness about antibiotic resistance and its consequences to promote the responsible use of antibiotics and encourage the development of new treatments. By working together, we can slow down the spread of antibiotic-resistant infections and preserve the effectiveness of antibiotics for years to come.
Consult a healthcare provider before opting for any antibiotic medication. For any queries or concerns, contact EliteCare, one of the best medical clinics in Florida, and schedule an appointment with our board-certified primary care physicians.