
World Health Day is observed on the 7th of April each year to raise awareness about important health issues affecting people worldwide. This year, the World Health Organization (WHO) is also celebrating its 75th anniversary on World Health Day. Therefore, it is worth bringing attention to a prevalent health concern that affects millions of people globally – type 2 diabetes. According to recent statistics, diabetes is the 8th leading cause of death in the United States1. Approximately 1 in 10 Americans are diagnosed with this condition, with 90-95% of them being specifically affected by type 2 diabetes2. In this blog post, we will learn more about type 2 diabetes, its risk factors and its detrimental effects on overall health.
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough of it. It is more common in adults, but it can also affect children and teenagers. Common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
Please note that some people may not experience any symptoms, especially in the early stages of the condition. Therefore, it is important to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to frequently monitor and manage blood sugar levels through Hb1Ac test.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes?
The pancreas is responsible for producing insulin, a hormone that is critical for regulating blood sugar levels. When carbohydrates are consumed, the body breaks them down and converts them into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream. In response to that, the pancreas secretes insulin to help cells in the body to absorb glucose from the food and use it for energy.
However, in individuals with type 2 diabetes, the body’s cells become resistant to insulin. As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream instead of being absorbed by cells, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes

There are several risk factors that can increase the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, such as:
Obesity
When there is an excess of fat, particularly around the abdominal region, it can release fatty acids into the bloodstream, which can impact the body’s ability to use insulin.
Physical inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle can increase insulin resistance, as regular exercise helps cells utilize glucose more efficiently.
Genetics
Variations in genes like TCF7L2 or PPARG can affect insulin secretion and glucose metabolism which can lead to type 2 diabetes.
Age
Age can also be a significant factor as cells in the body become less responsive to insulin over time. Individuals over the age of 45 are more likely to suffer from this condition.
Ethnicity
Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics and Native Americans are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Please note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that an individual will develop type 2 diabetes, but it does increase the likelihood significantly. It is important for people that are at risk for type 2 diabetes to visit their nearest health and wellness center to receive medical advice and appropriate treatment.
Health Complications Associated with Type 2 Diabetes
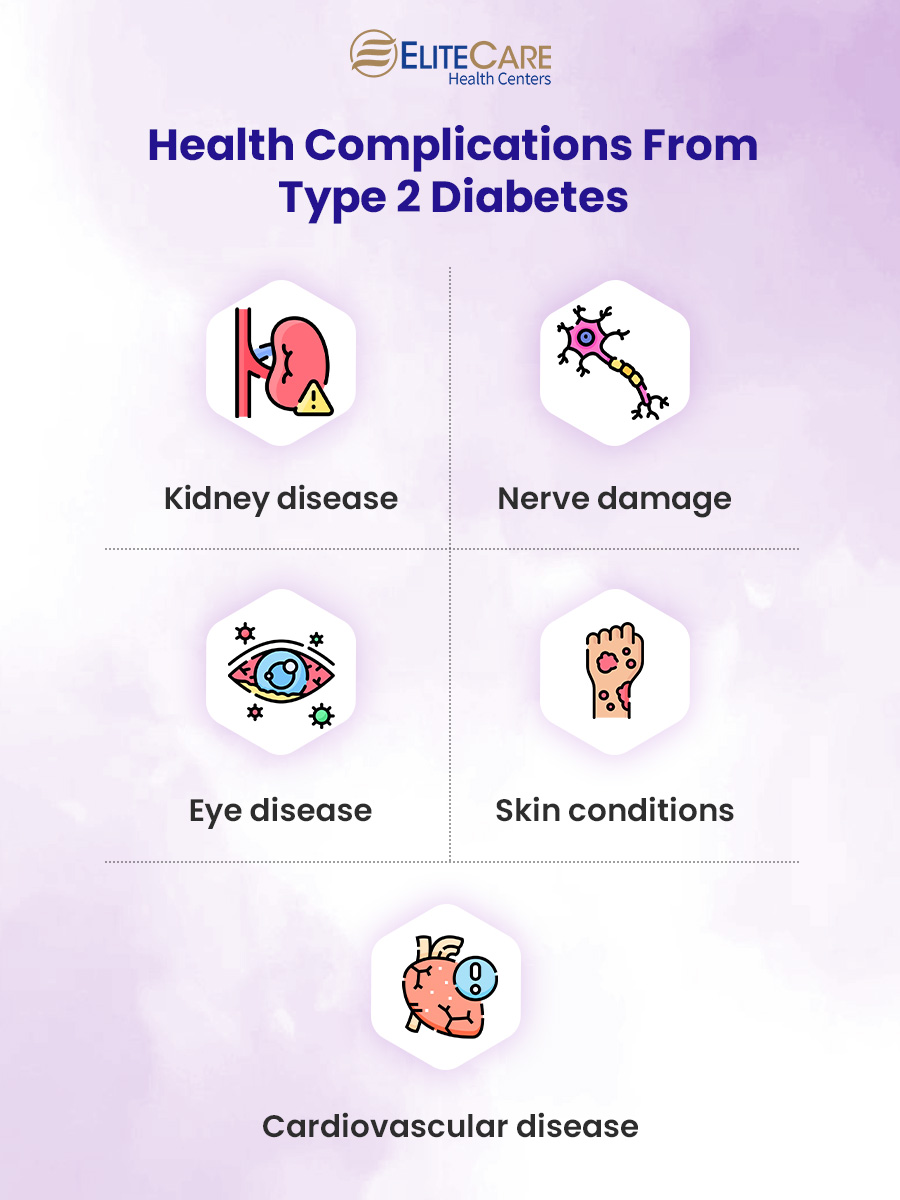
Type 2 diabetes can cause a range of health complications, some of which can be potentially life threatening. They include:
Cardiovascular Disease
People with type 2 diabetes are at a higher risk of suffering from a heart attack, stroke and peripheral artery disease as high sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart.
Kidney Disease
Diabetes damages the small blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the body. If left untreated, it can lead to kidney failure, a condition that may require life-long dialysis or a kidney transplant to effectively treat.
Nerve Damage
High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves in the body, leading to a condition called diabetic neuropathy. It typically affects the nerves in the feet and legs but can also affect the nerves in the arms and hands.
Eye Disease
Diabetes can also damage the small blood vessels in the eyes, leading to a condition called diabetic retinopathy which can cause vision problems, including partial or complete blindness.
Skin Conditions
People with diabetes are at higher risk of developing skin conditions, including bacterial and fungal infections. They may also suffer from diabetic dermopathy, a condition which causes patches of skin to become scaly and discolored.
Additionally, people suffering from type 2 diabetes have a higher likelihood of developing wounds and infections that are slow to heal due to nerve damage and poor blood circulation. As a result, they may experience reduced sensitivity in their extremities, making it harder to detect cuts, sores, or other injuries that require medical attention.
Therefore, individuals with type 2 diabetes must take proper care of their wounds, keep a close eye on their blood sugar levels, and work with their healthcare provider to manage their condition so as to prevent potentially deadly health complications.
8 Ways to Manage Type 2 Diabetes Better
The management of type 2 diabetes requires the implementation of various lifestyle changes, some of which include:
- Eating a healthy diet that is low in sugar, saturated fat, and salt
- Getting regular exercise
- Maintaining a healthy BMI
- Quitting smoking
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
- Getting quality sleep
- Managing stress levels
- Taking medications as prescribed
Type 2 diabetes requires a holistic approach that encompasses both lifestyle changes and medical interventions. To prevent the condition from worsening, it is crucial to follow medical advice closely.
Conclusion
In the United States, Diabetes is the leading cause of lower limb amputations and adult-onset blindness. Studies estimate that the total number of people currently affected by this condition (537 million) could increase by 46% by the year 2045. With such a substantial population at risk, it is important to raise awareness about this condition and its effect on health and wellbeing. It is essential for people suffering from type 2 diabetes to make appropriate lifestyle changes and strictly adhere to any medication regimen prescribed by their physician. Taking proactive steps early on to manage the condition can help individuals prevent or mitigate potentially deadly health complications associated with this illness.
If your elderly loved one is at risk for type 2 diabetes, visit the nearest health care center or EliteCare clinic for a blood draw to monitor and manage their blood sugar levels. EliteCare is one of Florida’s best medical clinics, with a team of highly trained primary care physicians who offer services like venipuncture, immunizations, EKG and more. Visit their website to schedule an appointment today.






