Multiple Sclerosis (MS), a chronic autoimmune disease, affects the central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. In this blog post, we will share various aspects of multiple sclerosis, including its symptoms and what affected individuals can do to prevent flare-ups. Read on to learn more.
What is Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
In this condition, the immune system attacks myelin, the protective covering of nerve fibers. As a result, it eventually leads to inflammatory reactions, disrupts the transmission of electrical impulses, and causes significant damage to the underlying nerves. Although researchers are still trying to figure out the exact cause of MS, it is believed to be a result of a combination of complex genetic and environmental factors.
Types of Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
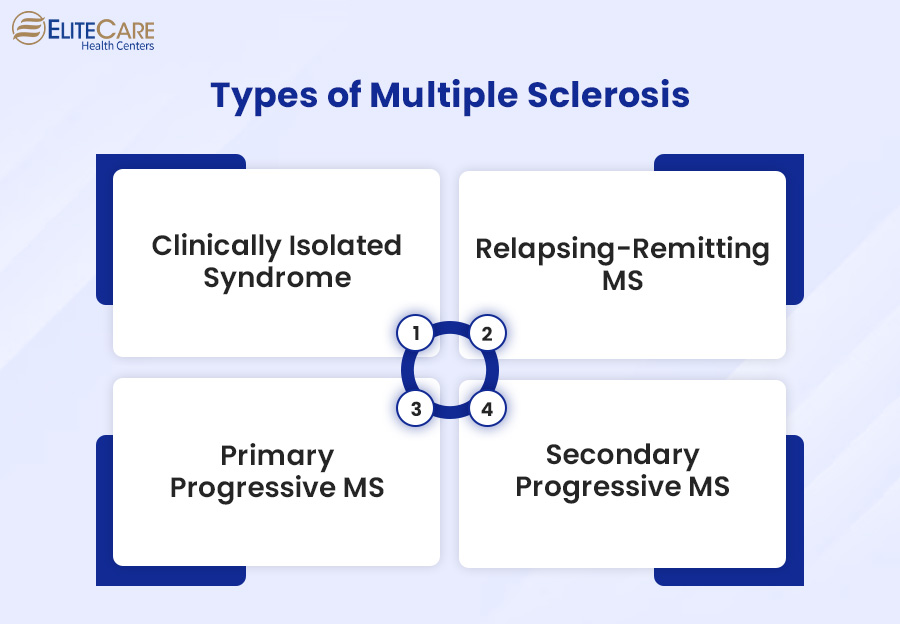
1. Clinically Isolated Syndrome
It is the first indication of neurological issues that lasts at least 24 hours. CIS most commonly causes optic neuritis or the inflammation of the optic nerve, and transverse myelitis, or the inflammation of the spinal cord. This condition is typically diagnosed using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
2. Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS)
This is the most common form of MS in which individuals have clearly defined attacks or relapses of neurological symptoms followed by periods of partial or complete recovery (remission). During remission, there is a lack of disease progression. RRMS symptoms can vary widely and may affect mobility, sensory functions, cognition, or other aspects of neurological function.
3. Primary Progressive MS (PPMS)
Individuals with Primary Progressive MS experience a gradual worsening of neurological function without distinct relapses or remissions. Symptoms of PPMS typically progress steadily over time. It may cause difficulty walking, muscle weakness, and problems with coordination and balance.
4. Secondary Progressive MS (SPMS)
In Secondary Progressive MS, there’s an initial period of relapsing and remitting. As time progresses, the signs of disability become more evident with or without any incidence of relapses and remissions.
Multiple Sclerosis Symptoms
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a complex neurological disorder, and the symptoms may vary depending on the type of MS and how far the disease has progressed. However, the following are some common symptoms that most people experience:
- Numbness or weakness in one or more limbs, typically affecting one side of the body at a time
- Tingling sensation in the body
- Electric-shock sensations along with bending the neck forward (Lhermitte sign)
- Lack of coordination
- Unsteady gait or inability to walk
- Pain during eye movement
- Prolonged double vision
- Blurry vision
- Vertigo
- Sexual dysfunction
- Problems with bowel and bladder function
- Fatigue
- Slurred speech
- Mood disturbances
- Difficulties with memory, attention, information processing speed, problem-solving, and multitasking
- Swallowing issues
These symptoms can vary in severity and may come and go (relapses and remissions), depending on the location of affected nerve fibers. In progressive forms of MS, symptoms may gradually worsen over time.
Therefore, individuals experiencing any of these symptoms should consult a primary care physician at the earliest for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management strategies.
Is MS Curable?
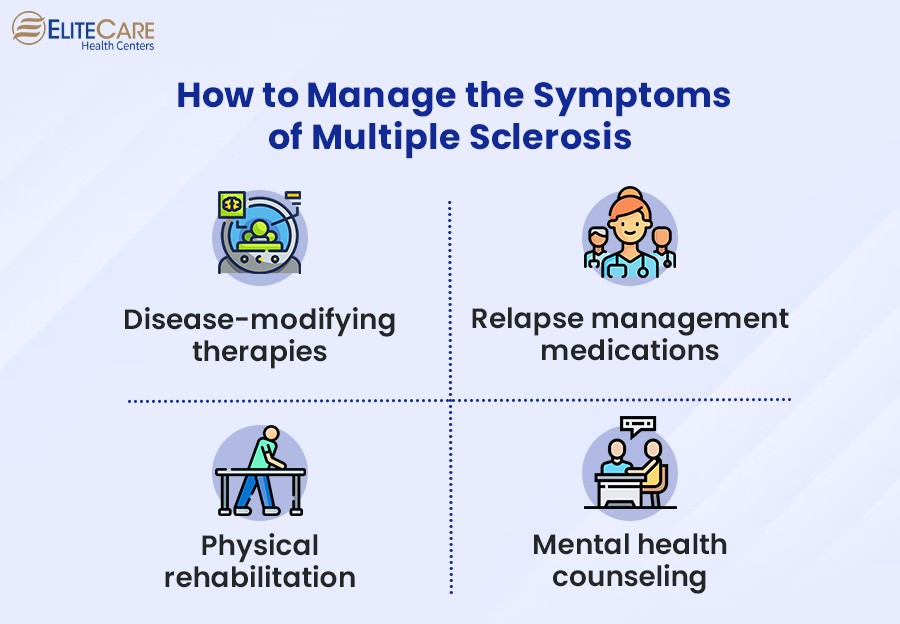
At present, it is not possible to completely cure Multiple Sclerosis (MS). However, there are various treatment approaches and clinical measures available to help individuals manage the symptoms, reduce relapses, and improve overall quality of life. The following are some common methods to manage MS:
1. Disease-Modifying Therapies (DMTs)
These therapies can help modify the course of MS by reducing the frequency and severity of relapses and slowing down the progression of disability. DMTs have also shown promising results in decreasing the number of brain lesions seen on MRI scans due to MS.
DMTs modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation in the central nervous system. There are several different types of DMTs available for the treatment of MS, and the choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of MS, individual preferences, and potential side effects.
2. Relapse Management Medications
Physicians usually prescribe these medications during relapses or exacerbations of MS symptoms. Short courses of corticosteroids are usually recommended to reduce inflammation and speed up the recovery process.
3. Physical Rehabilitation
It plays a key role in promoting functional abilities in individuals suffering from MS. Physical rehabilitation approaches can enhance mobility by improving strength, balance, and coordination.
The following are some common physical rehabilitation recommendations for MS:
- Physical Therapy (PT): It may include exercises targeting specific muscle groups, gait training, range of motion exercises, and functional training to enhance activities of daily living.
Read More: Benefits of Physical Therapy for Seniors
- Occupational Therapy (OT): It may focus on enhancing skills related to self-care tasks (such as bathing, dressing, and grooming), home management, and work-related activities to improve independence and functional abilities in daily activities.
- Balance and Coordination Training: It may involve activities such as balance exercises, proprioceptive training, coordination drills, Tai chi, and yoga.
- Aquatic Therapy: It involves exercises and movements performed in a pool or water environment to reduce the impact of MS on joints.
- Speech therapy: It can assist individuals experiencing speech or swallowing difficulties.
4. Mental Health Counseling
A chronic condition like MS can take a significant toll on mental well-being. Therefore, individuals may consider mental health counseling or psychotherapy to cope with the emotional challenges of MS. Counseling is a very useful tool that helps manage stress, address anxiety or depression, and enhance overall psychological well-being.
In addition, various medications and interventions can help manage specific symptoms associated with MS. For instance, doctors may consider prescribing muscle relaxants for spasticity, or pain medications for pain relief. Assistive devices such as mobility aids, braces, or wheelchairs can also help in improving mobility and independence.
The treatment approach for MS differs for every individual and a primary care physician can help create a comprehensive and personalized plan according to individual health requirements.
The Bottom Line
According to the National Insitute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, approximately one million people in the United States have MS. The unpredictable nature of the disease, characterized by periods of relapse and remission, can lead to significant challenges in managing symptoms, especially if it has already progressed. Therefore, it is crucial to know its symptoms and consult a primary care physician for proper diagnosis and treatment.
For any queries or concerns about Multiple Sclerosis, contact EliteCare Health Centers, one of the best medical clinics in Florida, offering a wide range of comprehensive senior care services, including venipuncture, routine annual exam, etc.