A voice disorder refers to any condition that affects the ability to produce or use one’s voice effectively. Some common symptoms of voice disorders are hoarseness, a weak voice, a sore throat, and difficulty in speaking. The cause of these symptoms can range from injury to disease to poor lifestyle habits. The high-risk group for voice disorders includes professionals who use their voice extensively such as teachers, singers, actors, and public speakers, as well as people who smoke, consume excessive alcohol, or are frequently exposed to loud noise. Loss of voice causes lack of self-confidence and it negatively affects the quality of life.
Why Are Seniors at Greater Risk?
Voice disorders are relatively common among older adults, and their prevalence keeps increasing as the population ages. According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD), approximately 20% of older adults in the US experience some form of voice disorder. It is because as the body ages, the muscles and tissues in the larynx (voice box) can weaken, making them more susceptible to damage.
Laryngeal cancer, one of the risk factors for vocal disorders, is more common among people between the ages of 55 and 84. Besides, Parkinson’s disease, ALS, or other neurological disorders can affect the ability to control the muscles used for speech, putting the elderly at an increased risk for voice disorders.
Types of Voice Disorders in Seniors
Dysphonia
It is a general term used to describe any disorder that affects the production of speech sounds and can manifest in many ways. Some examples of dysphonia include hoarseness, a weak voice, and difficulty speaking. A number of factors can cause dysphonia in seniors, including injury, disease, and lifestyle habits, such as smoking, exposure to loud noise, and overuse of the voice.
Dysarthria
It is a motor speech disorder caused by neurological damage that affects the muscles that control and coordinate speech. Symptoms can include slurred speech, difficulty controlling the pitch, rate, or volume of speech, and problems with pronunciation. It is also common in neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and other conditions that can affect the muscles used for speech.
Presbyphonia
It is a type of age-related change in the voice, characterized by changes in pitch, volume, and overall quality of the voice. Presbyphonia is caused by the gradual deterioration of the muscles and tissues in the larynx (voice box) as we age.
How to Diagnose Voice Disorders?
Diagnosing a voice disorder typically involves taking a thorough medical history of the patient, performing a physical exam, and possibly ordering imaging tests. Doctors initially perform a physical examination by looking at the patient’s throat and larynx (voice box) with a special lighted instrument called a laryngoscope. They may also feel the patient’s neck and palpate the larynx to check for any lumps or nodules.
Depending on the suspected cause of the voice disorder, the doctor may order additional tests such as x-rays, MRI or CT scans, or a laryngoscopy. These imaging tests can help to provide a clearer view of the patient’s larynx, vocal cords, and other structures in the throat. These tests also allow the doctor to identify any abnormalities that may be causing the voice disorder.
What Are the Treatment Options for Voice Disorders?

Treatment options for voice disorders vary depending on the cause and severity of the issue, but may include:
Speech therapy
It is the most common treatment for voice disorders used to improve the function and quality of the voice. The speech therapist will work with the patient to help them learn how to use their voice more effectively. In addition, they may teach exercises and techniques to improve the strength and flexibility of the vocal cords.
Medication
Depending on the cause of the voice disorder, the doctor may prescribe medication to alleviate symptoms. For example, if acid reflux is the reason behind the disorder, the doctor may recommend antacids or proton pump inhibitors to help control acid reflux. If an infection is causing the disorder, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics or antiviral medication.
Surgery
If a benign growth, such as a vocal cord nodule or polyp, is causing the disorder, doctors may suggest excising the growth surgically. If cancer has caused the disorder, surgery can be used to remove the cancerous tissue. Surgery for voice disorders typically involves a procedure called a laryngectomy, which removes part or all of the larynx.
It is critical to note that the success of the treatment will depend on the underlying cause and the stage of the voice disorder. In order to tailor the most appropriate treatment plan for each patient, individual needs and circumstances should be kept in mind. It is also important for patients to work closely with their doctors and speech therapists to ensure that the treatment plan is appropriate and effective.
4 Ways to Manage Voice Disorders in Seniors
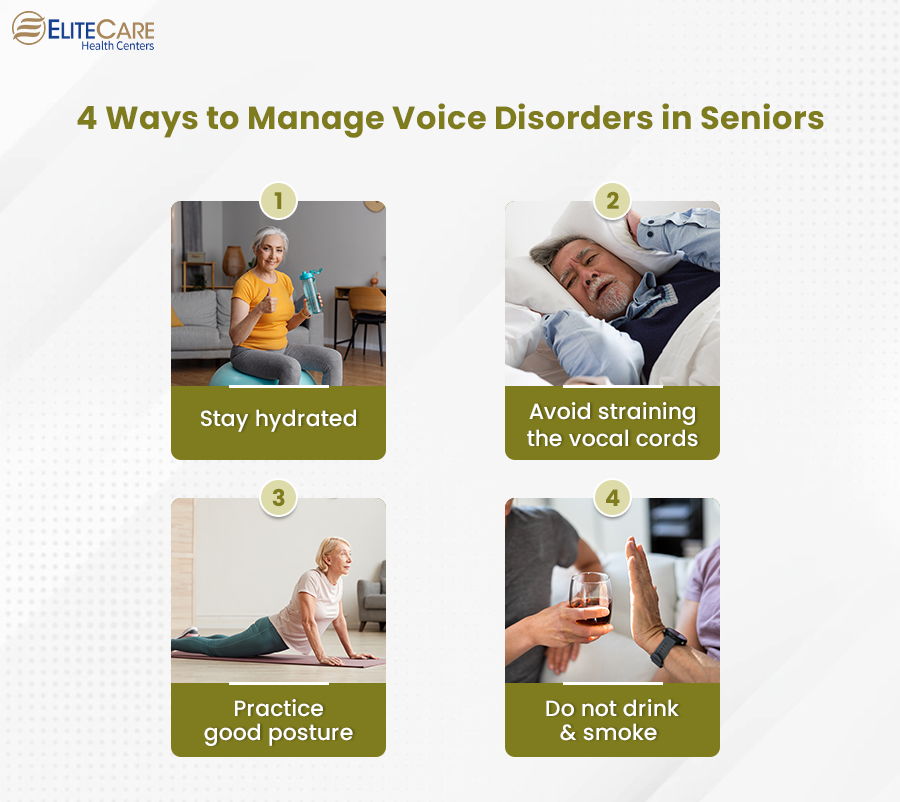
1. Stay hydrated
Drinking plenty of fluids, particularly water, can help to keep the vocal cords healthy and prevent voice disorders. Adequate hydration enables the body to produce more mucus that protects and moisturizes the vocal cords. In return, it allows them to vibrate more easily and produces more consistent voice quality. When the vocal cords become dehydrated, they can become dry and less elastic, which can make them more susceptible to injury or damage.
Remember that the recommended daily water intake can vary for individuals based on age, sex, activity level, and overall health. However, a general guideline is to drink at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water per day. It is also helpful to keep in mind that some foods like fruits, vegetables, and soups also help to hydrate the body.
2. Avoid straining the vocal cords
Shouting or overusing the voice can put extra strain on the vocal cords and lead to injury or damage. Limit exposure to loud noise, as it can cause irritation and damage to the vocal cords. Speak at a moderate volume and take regular breaks if seniors are using their voices frequently.
Also, ask seniors to warm up their voices before using them for extended periods of time by humming or making lip trills.
3. Practice good posture
Slouching can cause tension in the neck and throat, which can affect the voice. By sitting and standing with the correct posture, seniors can help to reduce tension in these areas and preserve the health of their vocal cords.
4. Do not drink and smoke
Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can cause inflammation and damage to the vocal cords. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption can dehydrate the body and dry out the vocal cords. Both habits can significantly increase the risk of voice disorders.
Conclusion
It is crucial for older adults to be aware of their risks and take steps to protect their voices and seek medical help if they notice any changes. Work closely with a doctor or a speech therapist to ensure that the treatment plan is appropriate and effective. It is crucial to remember that voice disorders can have a significant impact on seniors’ quality of life, making it difficult to communicate with others and affecting their participation in social activities. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life of patients suffering from voice disorders.
If a senior member of your family is noticing any symptoms of voice disorders, contact EliteCare Health Centers, one of the best medical clinics in Florida and consult the best primary care physicians in Florida.